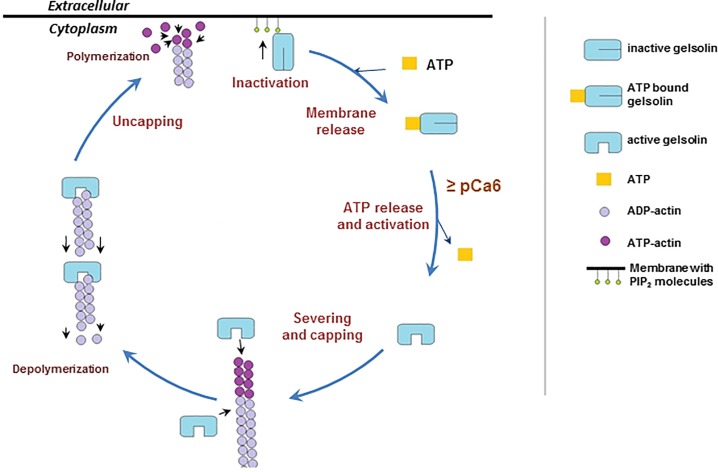
Fig 4. Model of the severing, capping, uncapping and inactivation/release cycle of gelsolin.
The cartoon presents a model for the cycle of activation and function of gelsolin. Severing and capping: Elevated free calcium levels activate gelsolin, releasing ATP, leading to severing and capping of actin filaments. Depolymerization: Gelsolin-capped filaments will depolymerize from their pointed ends. Uncapping and polymerization: Gelsolin-capped actin filaments will be uncapped on encountering PIP2 in the membrane, resulting in force being exerted on the membrane from the polymerization of the uncapped filaments. Inactivation and membrane release: Gelsolin will be released from PIP2 and the membrane by competition with ATP. Following its release gelsolin is able to undergo subsequent cycles of severing, capping, uncapping and inactivation/release.