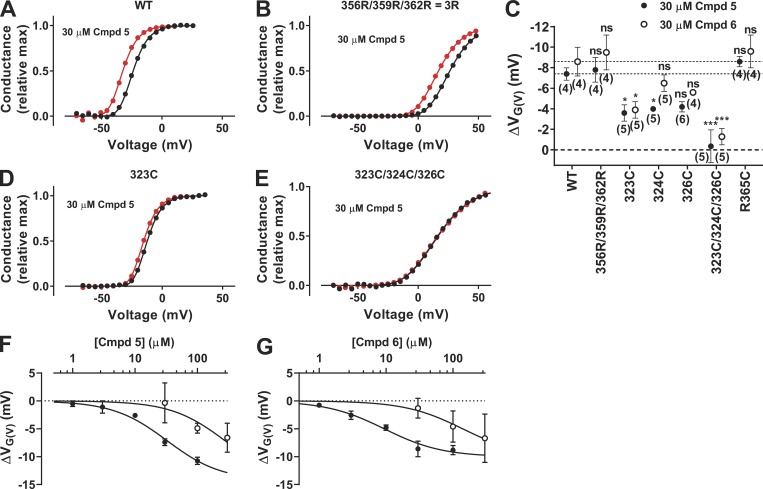
Figure 7.
Mutational effect on Cmpd 6– and Cmpd 5–induced G(V) shifts. (A, B, D, and E) Representative effect of 30 µM Cmpd 5 on the G(V) curve of four different WT or mutated Shaker KV channels. Data fitted to Eq. 2 with the exponent n = 4. ΔVG(V) = −8.6 mV (A), −9.4 mV (B), −3.0 mV (D), and −0.4 mV (E). (C) Summary of data from all mutations. n = 4–6; mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test to compare the effect of Cmpd 5 or Cmpd 6 on each mutant to the corresponding effect on the WT Shaker KV channel. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ns, P > 0.05. Dashed lines denote WT data. (F and G) Dose–response curves for Cmpds 5 and 6 on WT (closed symbols, data from Fig. 6) and the triple mutant Y323C/F324C/T326C (open symbols; mean ± SEM, n = 3–5). Best fit of Eq. 3 with ΔVG(V),max constrained to be equal for WT and the triple mutant. (F) ΔVG(V),max = −14.3 ± 2.3 mV; c1/2(WT) = 32 ± 14 µM; c1/2(Y323C/F324C/T326C) = 276 ± 96 µM. (G) ΔVG(V),max = −10.0 ± 1.1 mV; c1/2(WT) = 9.4 ± 1.8 µM; c1/2(Y323C/F324C/T326C) = 141 ± 52 µM.