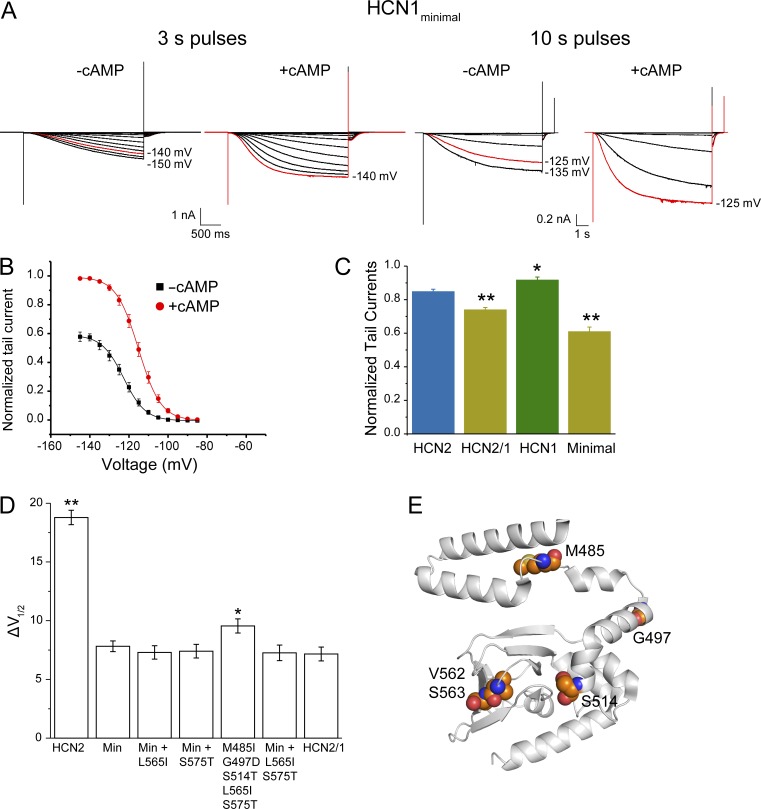
Figure 4.
The voltage-dependent modulation of the HCN1minimal mutant (with substitutions M485I, G497D, S514T, V562A, and S563G) is similar to the HCN2/1 chimera. (A) Representative traces of inside-out recordings for the HCN1minimal mutant in the absence and presence of 10 µM cAMP. For comparison, because of the slow kinetics in this mutant, recordings obtained with 10-s voltage pulses to ensure that the currents are saturated even in absence of cAMP are shown. (B) Conductance–voltage curves for the HCN1minimal mutant normalized to the maximum tail current in the presence of cAMP. (C) Tail currents at saturating voltages in absence of cAMP for WT HCN2 (n = 14 patches), WT HCN1 (n = 21), HCN2/1 (n = 19), and the HCN1minimal mutant (n = 21), calculated relative to the maximum tail current in saturating voltages and cAMP for each patch. *, P = 0.01; **, P < 0.00003 compared with WT HCN2. (D) Additional mutations L565I and S575T do not affect cAMP-dependent ΔV1/2 in the HCN1minimal (Min) background. n = 19 for WT HCN2, 21 for HCN1minimal, 19 for Min + L565I, 18 for Min + S575T, 17 for M485I G497D S514T L565I S575T, 20 for Min + L565I S575T, and 19 for HCN2/1. *, P = 0.03; **, P = 5 × 10−17 versus the HCN1minimal mutant. For conductance–voltage curves, see Fig. S3. Data presented are mean ± SEM. (E) HCN2 structure (PDB accession no. 3U10) showing the residues mutated in the HCN1minimal mutant (Lolicato et al., 2011).