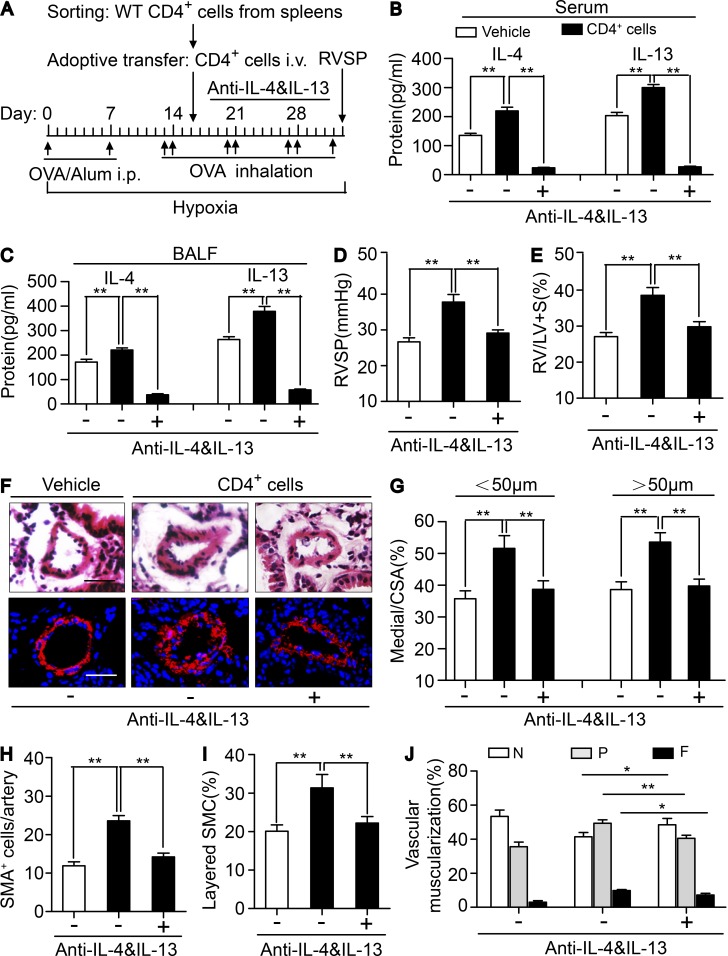
Figure 7.
Neutralization of IL-4 and IL-13 reversed infusion of CRTH2+/+ CD4+ T cells exaggerated PAH in CRTH2−/− mice. (A) Schematic representation of the protocol for administration of CRTH2+/+ CD4+ T cell–infused CRTH2−/− mice to induce PAH. (B and C) Protein levels of IL-4 and IL-13 in the serum (B) and BALF (C) from HyOA-treated mice after CRTH2+/+ CD4+ T cell infusion with or without dual neutralization of IL-4 and IL-13. (D and E) Effect of neutralization of IL-4 and IL-13 on RVSP (D) and RV/LV + S ratio (E) in CRTH2+/+ CD4+ T cell-infused CRTH2−/− mice. (F) Representative images of H&E staining and SMA (red) immunostaining of PAs of CRTH2+/+ CD4+ T cell–infused mice with or without dual neutralization of IL-4 and IL-13. Bar, 20 µm. (G) Quantification of the ratio of pulmonary arterial medial thickness to total vessel size (media/CSA) for the CRTH2+/+ CD4+ T cell–infused mice with or without dual neutralization of IL-4 and IL-13. (H and I) Quantification of the number (H) and percentages (I) of layered SMCs in PAs from CRTH2+/+ CD4+ T cell–infused mice with or without dual neutralization of IL-4 and IL-13. (J) Proportion of nonmuscularized (N), partially muscularized (P), or full muscularized (F) pulmonary arterioles (20–50 µm in diameter) from CRTH2+/+ CD4+ T cell–infused mice with or without dual neutralization of IL-4 and IL-13. In A–J, n = 8–10 mice per group. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 as indicated. All graphs are shown as mean ± SEM. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined using unpaired Student’s t tests.