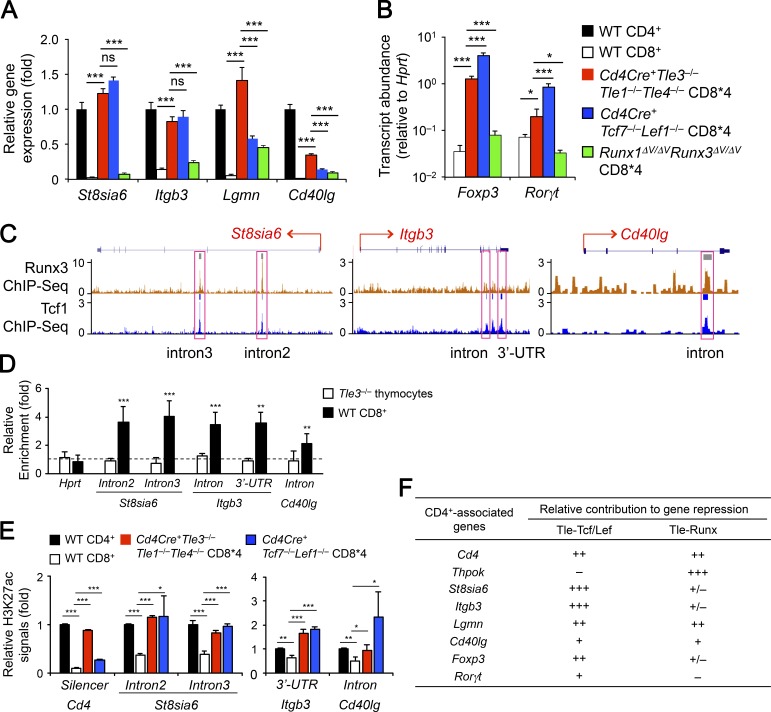
Figure 7.
The Tcf/Lef-Tle complex has a broader role in repressing CD4+ lineage-associated genes in mature CD8+ T cells. (A and B) Comparative analysis of CD4+ lineage-associated genes upon loss of Tle1/3/4, Tcf1/Lef1, and Runx-Tle interactions. CD8*4 cells were sorted from TCRβ+ splenocytes in Cd4Cre+Tle3−/−Tle1−/−Tle4−/−, Cd4Cre+Tcf7−/−Lef1−/− or Runx1ΔV/ΔVRunx3ΔV/ΔV mice, along with splenic CD4+ and CD8+ SP T cells from WT mice, and analyzed for the expression of indicated CD4+ lineage-associated genes. For each of CD4+ signature genes in A, its expression in WT CD4+ T cells was set at 1, and its relative expression in other samples was normalized accordingly. Because conventional CD4+ T cells do not express Foxp3, the relative abundance of Foxp3 and Rorγt transcripts in WT CD8+ or various CD8*4 cells were compared directly without normalization to WT CD4+ cells. Data are means ± SD from two experiments (n = 2–3, with each sample measured in duplicates). Statistical significance among multiple groups was first assessed with one-way ANOVA coupled with Bonferroni correction. ns, not statistically significant; *, P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 by Student’s t test for indicated pairwise comparison. (C) Tcf1 and Runx3 ChIP-Seq tracks at the St8sia6, Itgb3, and Cd40lg loci in CD8+ T cells. Tcf1 and Runx3 ChIP-Seq data in CD8+ T cells were retrieved from GSE73240 and GSE50131, respectively, and loaded on UCSC genome browser, with horizontal bars on top of each track denoting MACS-called binding peaks. Pink rectangles mark Tcf1 binding peaks that were assessed for Tle3 binding (D) and H3K27ac signals (E). (D) Enriched Tle3 binding at Tcf1-occupied sites in select CD4+ signature genes. Tle3 ChIP was performed on WT splenic CD8+ T cells with VavCre+Tle3−/− total thymocytes as a negative control, and relative enrichment of Tle3 binding was determined at the indicated genomic locations. Data are means ± SD from three to four experiments. Dotted line marks no enrichment. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 by Student’s t test. E. Tcf1- and Tle3-cooccupied sites are hyperacetylated in CD8+ T cells lacking Tcf1/Lef1 or Tle1/3/4. Cells were sorted as in A and subjected to H3K27ac ChIP analyses at indicated genomic locations. The H3K27ac signal was first normalized to chromatin input in each cell type, and that in WT CD4+ T cells was set as 1, with relative H3K27ac in other cell types normalized accordingly. Data are means ± SD from two independent experiments with each ChIP sample measured in duplicates or triplicates. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 by Student’s t test compared with WT CD8+ T cells. (F) Deduced relative contribution of Tcf/Lef-Tle and Runx-Tle complexes to repression of CD4+ signature genes in CD8+ T cells, based on data in Figs. 6 and 7.