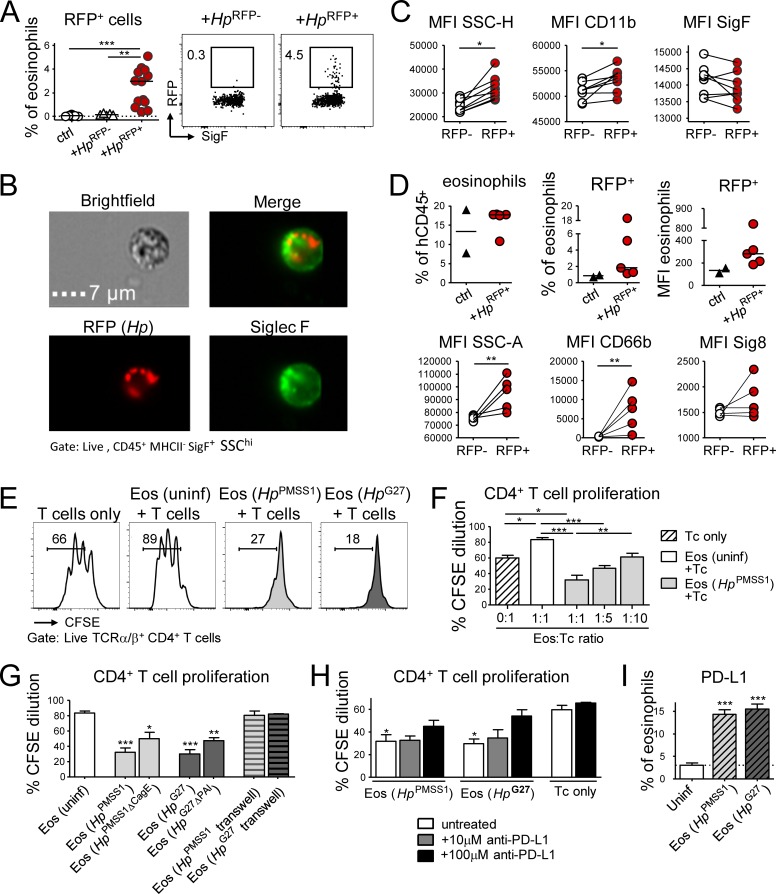
Figure 4.
Eosinophils encounter RFP+H. pylori in the gastric LP and suppress T cell proliferation in a PD-1/PD-L1–dependent manner. (A–C) Mice were infected at 1 wk of age with RFP+ or WT (RFP−) H. pylori for 3 mo. (A) Frequency of RFP+ eosinophils among all gastric LP eosinophils. Representative FACS plots are shown along with the quantification of two pooled experiments. (B) Representative ImageStream-derived image of a SiglecF+ eosinophil that colocalizes with multiple RFP+ bacteria. Bar, 7 µm. (C) Activation state of RFP+ relative to RFP− eosinophils of the same stomach of the mice shown in A. (D) Mice were reconstituted at birth with human cord blood HSCs and infected at 4 wk of age with RFP+ H. pylori for 6 wk; frequencies of human eosinophils among all human CD45+ leukocytes, and of RFP+ human eosinophils among all human gastric LP eosinophils are shown in the top panel. The MFI of the RFP channel is also shown. Bottom panel: activation state of RFP+ relative to RFP− human eosinophils of the same stomach, as judged by CD66b and Siglec-8 expression and granularity. (E–H) Naive or H. pylori–infected, in vitro differentiated eosinophils were co-cultured at 1:1 or the indicated ratios with CSFE-labeled immunomagnetically isolated splenic CD4+ T cells in the presence of anti-CD3/CD28-coated beads, IL-2, and IL-5. Two different strains of H. pylori (PMSS1 and G27) were used in parallel to infect eosinophil cultures for 18 h. (E) Representative FACS plots of the CFSE dilution of anti-CD3/CD28 bead-activated T cells relative to T cells co-cultured with naive or H. pylori–educated eosinophils. (F) Quantification of the CFSE dilution of T cells co-cultured with the indicated eosinophil:T cell ratios. (G) Quantification of the CFSE dilution of T cells co-cultured with eosinophils that had previously been exposed to the indicated WT and mutant H. pylori strains, with and without separation by a trans-well filter. (H) Quantification of the CFSE dilution of T cells in eosinophil co-cultures, in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of anti–PD-L1 blocking antibody. Means +SEM of three technical replicates of one representative experiment of two or three are shown in F–H. (I) PD-L1 expression of eosinophils infected with the indicated H. pylori strains for 18 h. Statistics were calculated by Mann-Whitney test in A–D and by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction in F–I and are relative to the control condition. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.