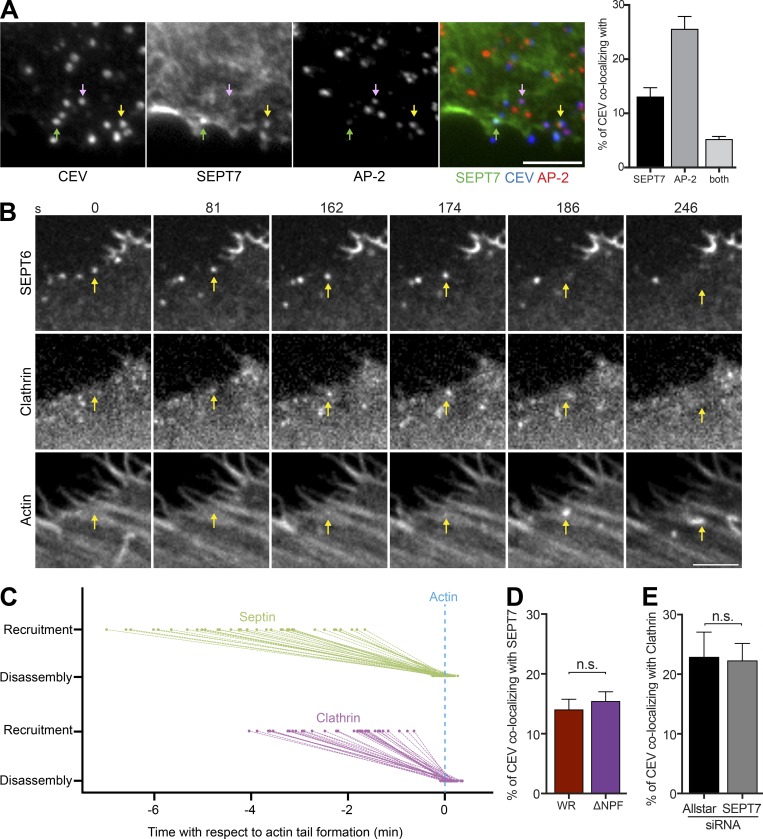
Figure 5.
Septin and clathrin are recruited independently to CEV. (A) Immunofluorescence images showing the association of SEPT7 (green arrow), AP-2 (pink arrow), or both proteins (yellow arrow) with CEV (detected with the B5 antibody before membrane permeabilization) in HeLa cells infected with WR for 8 h. The graph shows percentage of CEV with SEPT7, AP-2, or both proteins. (B) Video stills taken from live cell imaging of WR-infected HeLa cells expressing GFP-SEPT6, mCherry-clathrin light chain (Clathrin), and LifeAct-iRFP (Actin). SEPT6 is recruited to CEV before clathrin, but both proteins are lost when actin polymerization starts. The time in seconds is indicated. See Video 4. (C) The graph shows the recruitment and loss of SEPT6 and clathrin to CEV with respect to actin tail formation. (D) The graph shows the percentage of CEV recruiting septin in the presence (WR) or absence (ΔNPF) of clathrin. (E) The percentage of CEV recruiting clathrin in the presence (Allstar) or absence of SEPT7. Bars, 5 µm. Error bars represent SEM from three independent experiments. For protein timings in C, 36 virus particles were analyzed, and for each of the other conditions, 900 CEVs were analyzed from 30 cells.