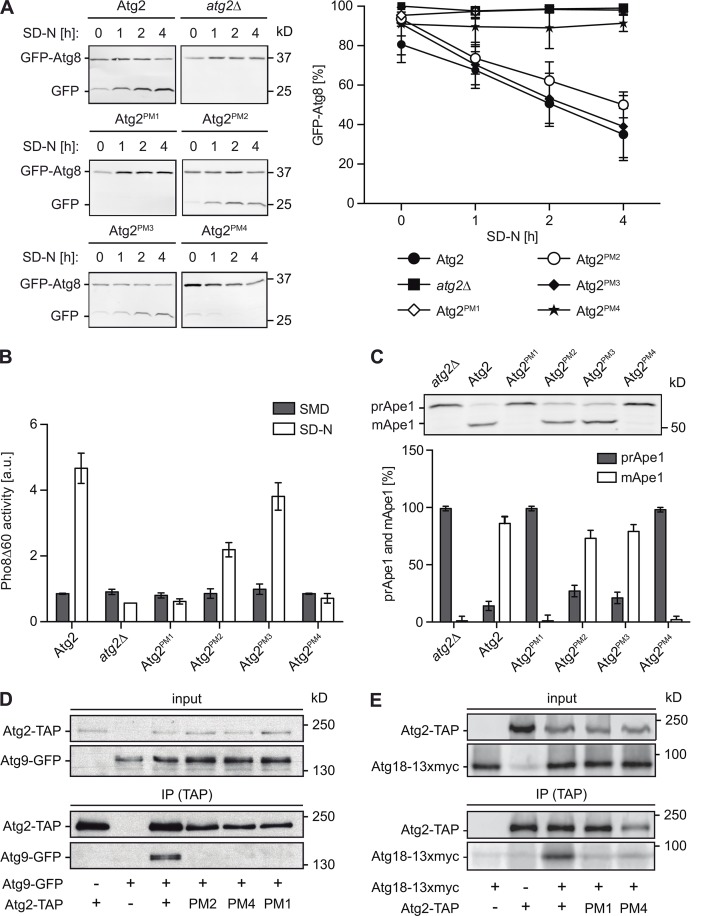
Figure 2.
Interaction between Atg2 and Atg9 is essential for both bulk and selective autophagy. (A) Mutations in the putative Atg9-binding region of Atg2 lead to a severe block of bulk autophagy. The atg2Δ cells (FRY375) carrying both the pCuGFPATG8414 vector and a plasmid expressing Atg2 or the different Atg2 point mutants or the empty vector pRS416 were grown in SMD to an early log phase and transferred to the autophagy-inducing SD-N. Culture aliquots were collected 0, 1, 2, and 4 h after autophagy stimulation, and cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting using an antibody against GFP. A graph representing the relative amount of the GFP-Atg8 chimera at each time point calculated from three independent experiments plus SD is shown on the right. Representative blots are shown on the left. (B) Defective autophagy caused by Atg2 mutations. The PHO8Δ60 atg2Δ strain (FRY388) was transformed with an empty vector (pRS416; atg2Δ) or plasmids expressing Atg2 or the different Atg2 point mutants. Transformed cells were cultured in SMD to early log phase and transferred into SD-N starvation medium for 4 h to induce autophagy. The Pho8Δ60 assay was performed as described in Materials and methods. (C) Mutations in the Atg9-binding region of Atg2 severely affect the cytosol-to-vacuole targeting pathway. Strains analyzed in A were cultured in SMD to early log phase. Samples were collected, and cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting using the anti-Ape1 antiserum. The detected bands were then quantified as in A, and the percentages of precursor and mature Ape1 (prApe1 and mApe1, respectively) were plotted. The presented data represent the means of three independent experiments ± SD. (D) The identified Atg2PM1, Atg2PM2, and Atg2PM4 mutants do not interact with Atg9 in vivo. Cell extracts from atg2Δ (yCK759) and atg2Δ Atg9-GFP (yDP191) strains transformed with an empty vector (pRS315) or plasmids expressing WT or point-mutated TAP-tagged Atg2, pATG2PM1-TAP, pATG2PM2-TAP, and pATG2PM4-TAP were subjected to pulldown experiments and analyzed as in Fig. 1 C. (E) Atg18 interaction with Atg2 requires Atg2 binding to Atg9. Cell extracts from atg2Δ (FRY375) and atg2Δ Atg18-13×myc strains transformed with an integrative empty vector (RSGY015) or plasmids expressing TAP-tagged versions of Atg2, Atg2PM1, or Atg2PM4 (RSGY012, RSGY013, and RSGY014) were subjected to pulldown experiments and analyzed with anti-myc and anti-TAP antibodies.