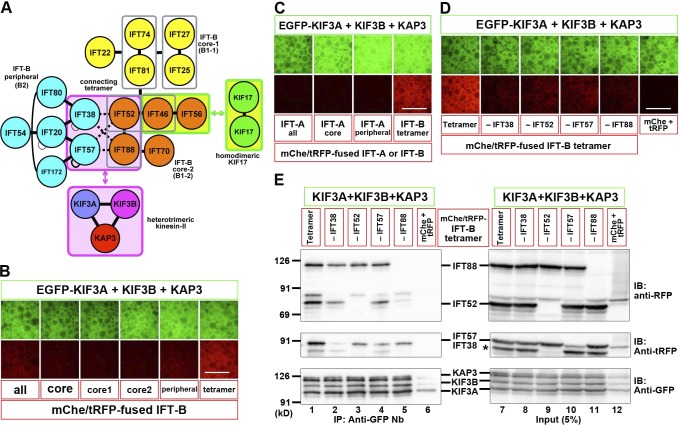
Figure 2.
Interaction of heterotrimeric kinesin-II with the IFT-B–connecting tetramer. (A) A model for the interaction of IFT-B with homodimeric KIF17 and heterotrimeric kinesin-II. (B) Identification of an interaction between heterotrimeric kinesin-II and the IFT-B–connecting tetramer. Lysates from cells coexpressing EGFP-fused kinesin-II subunits and all IFT-B subunits, subunits of all core, core 1, core 2, or peripheral subcomplexes, or connecting tetramer fused to mChe/tRFP were processed for the VIP assay. (C) Lack of an interaction between the IFT-A complex and heterotrimeric kinesin-II. Lysates from cells coexpressing EGFP-fused kinesin-II subunits and mChe-fused IFT-A subunits (all, core, or peripheral) were subjected to the VIP assay. (D and E) Subtractive VIP assay and immunoblotting (IB) analysis to determine subunits of the IFT-B–connecting tetramer required for its interaction with kinesin-II. Lysates from cells coexpressing EGFP-fused kinesin-II subunits and all but one (as indicated) subunits of the IFT-B tetramer fused to mChe/tRFP were processed for the VIP assay (D) or immunoblotting analysis (E) using the following antibodies: an anti-RFP antibody (top), which reacts with mChe; an anti-tRFP antibody (middle), which reacts with tRFP and cross-reacts with the mChe portion of mChe-IFT52 (indicated by an asterisk); or an anti-GFP antibody (bottom). Note that the bands for tRFP-fused IFT38 and IFT57 were overlapped with each other. As a negative control, a mixture of mChe-fused and tRFP-fused IFT56 was used in place of mChe/tRFP-fused tetrameric subunits (labeled as mChe+tRFP). Bars, 100 µm.