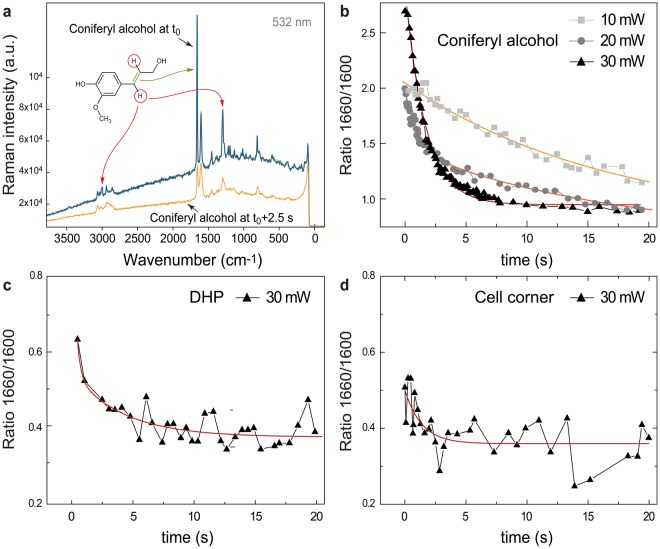
Figure 3.
Spectral changes of coniferyl alcohol under laser exposure and time series of reference model compounds taken with λex = 532 nm. (a) Raman spectra of coniferyl alcohol at t0, meaning measured at the earliest time possible, and at t0 + 2.5 s, with a laser power of 30 mW. The Raman bands affected are marked with an arrow depicting the functional groups that undergo a modification upon laser exposure in coniferyl alcohol. Most notably is the decrease of the C=C stretch at 1660 cm−1. Also two bands representing the C–H stretch (3013 cm−1) and bend (1297 cm−1) lose intensity. New bands around 2914 cm−1 (unsaturated C–H stretch) arise. Raman band intensities at 1600 and 1660 cm−1 measured over time from the three substances were used to calculate the ratio 1660/1600 displayed in (b) for coniferyl alcohol, for laser powers of 10, 20 and 30 mW, and (c) DHP and (d) cell corner of spruce wood, for a laser power of 30 mW. The ratio decay followed an exponential trend for all compounds. An exponential decay function was used to fit the ratio over time for all three compounds. For coniferyl alcohol, a stronger decay was observed the higher the laser power. The fitting parameters are displayed in Table 1.