Fig. 3.
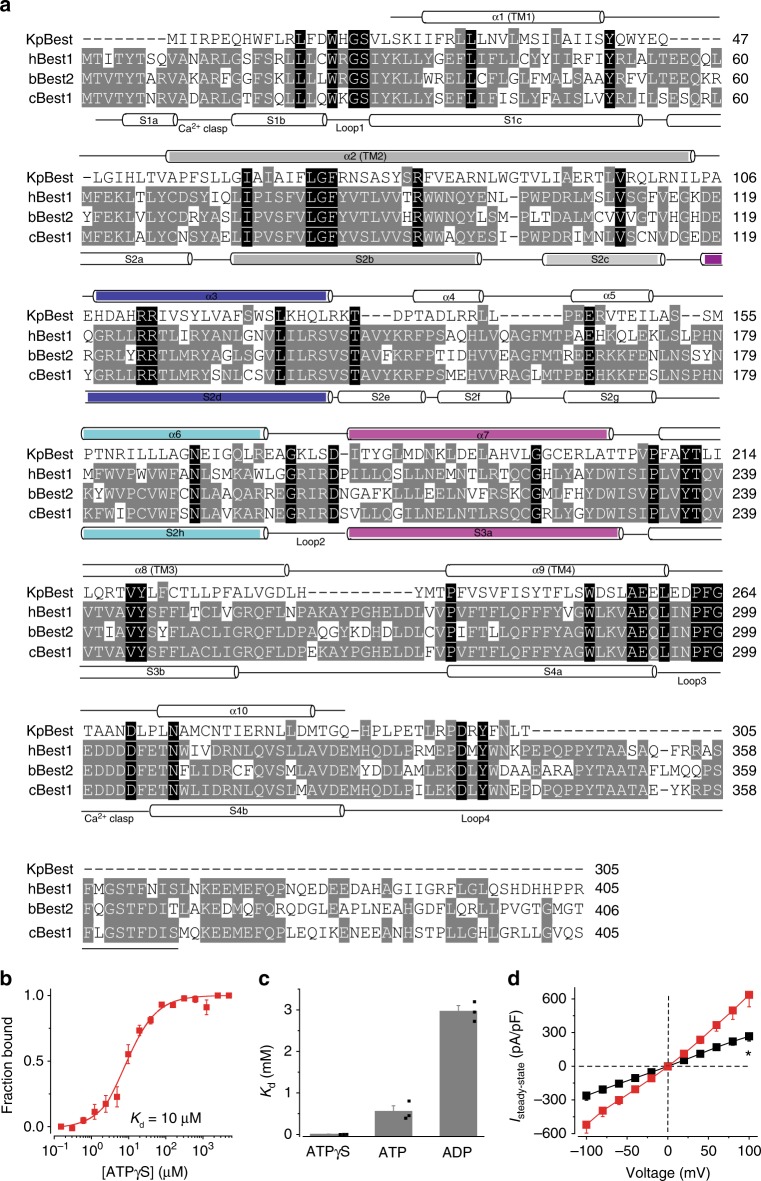
ATP interacts with and activates bBest2. a Structure-based sequence alignment of KpBest, hBest1, bBest2, and cBest1. The KpBest structure is used to restrict sequence gaps to interhelical segments. Black background, identical residues in all four species; gray background, identical residues in two or three species. The secondary structures of KpBest and cBest1 are labeled above and below the sequences, respectively. The four loops (1–4) potentially involved in ATP binding are labeled below the cBest1 secondary structure. Critical helices potentially involved in channel activation are highlighted in the same colors as those in Fig. 7. b The MST binding curve of bBest2 to ATPγS. Protein fraction bound vs. [ATPγS], n = 3 for each point. c Bar chart showing the binding affinities of bBest2 to ATP analogs. n = 3 for each bar. d Population steady-state current–voltage relationships of bBest2 transiently expressed in HEK293 cells without (black) or with (red) ATP (10 mM), n = 9–13 for each point. *P < 0.05 compared to cells in the presence of ATP, using two-tailed unpaired Student t test. All error bars in this figure represent s.e.m.