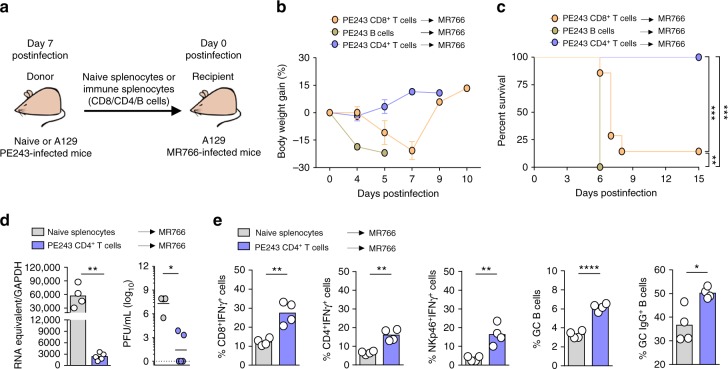
Fig. 4.
CD4+ T cell plays an essential role in the resistance against ZIKV MR766 infection. Recipient A129 mice were inoculated intravenously with 2 × 105 PFU of lethal ZIKV strain MR766 simultaneously to the receipt of CD8+ T cells, B cells or CD4+ T cells obtained from ZIKV strain PE243-infected A129 donor mice at 7 days postinfection. Uninfected mice were used as donor of naive splenocytes. a Schematic representation of adoptive transfer protocol. b Body weight gain and c lethality of recipient A129 mice that received PE243-immune CD8+ T cells (1 × 107/mouse) (n = 7), CD4+ T cells (4–5 × 107/mouse) (n = 9) or B cells (1 × 107/mouse) (n = 4), monitored for up to 15 days postinfection. d ZIKV RNA copies and presence of ZIKV infectious particles in the brain of recipient mice that receive PE243-immune CD4+ T cells (n = 5) or naive splenocytes (n = 4) at 5 days postinfection determined by qRT-PCR and plaque assay, respectively. Results are expressed as RNA equivalent/copies and normalized by GAPDH and as PFU/mL for qRT-PCR and plaque assay, respectively. The horizontal dotted line indicates the limit of detection. e Spleens were retrieved from recipient A129 mice that received naive splenocytes (n = 4) or PE243-immune CD4+ T cells (n = 4) at 5 days postinfection for flow cytometry’s assays. Relative frequency of IFNγ producing CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells and NKp46+ as well as germinal center B cells and IgG producing B cells. Results are shown as mean in d and e or as mean ± standard deviation in b. Data are presented as a pool of two independent experiments in b and c, experiment were performed once in d and e. Survival data were analyzed by Log rank test. Data were analyzed by Student’s t-test in d and e. * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; **** p ≤ 0.0001