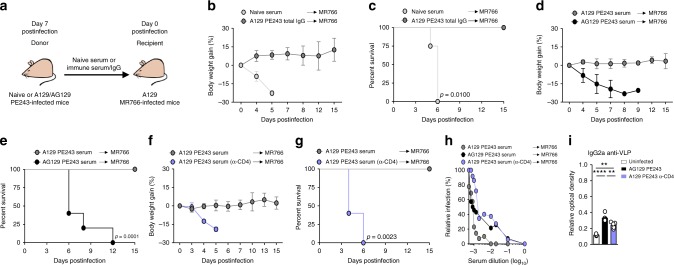
Fig. 6.
Serum of ZIKV PE243-infected A129 mice protects against ZIKV MR766 infection. a Schematic representation of passive serum administration. b Body weight gain and c lethality of recipient mice that received PE243 purified IgG (35.7 mg/kg) (n = 4) or naive serum (n = 4) were monitored for up to 15 days postinfection. d Body weight gain and e lethality of recipient mice that received serum from PE243-infected A129 mice (n = 8) or AG129 mice (n = 5) were monitored for up to 15 days postinfection. f Body weight gain and g lethality of recipient mice that received serum from PE243-infected A129 mice previously depleted of CD4+ T cells (n = 5) or not (n = 5) were monitored for up to 15 days postinfection. h Pooled sera from A129 or AG129 mice infected with ZIKV PE243 as well as infected A129 mice previously depleted of CD4+ T cells were collected, serially diluted and incubated with ZIKV MR766. Infectivity was determined by plaque assay. i Serum IgG2a anti-ZIKV VLPs in uninfected mice (n = 3), ZIKV strain PE243-infected AG129 mice (n = 6) and ZIKV PE243-infected A129 mice previously depleted of CD4+ T cells (n = 5). Results are represented as relative optical density by performing the ratio with ZIKV strain PE243-infected A129 mean value . Results are shown only as mean in i or as mean ± standard deviation in b, d, and f. Data are presented as a pool of two independent experiments in b–g or as representative of two independent experiments in h and i. Survival data were analyzed by log rank test. Data were analyzed by Student’s t test in i. ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; **** p ≤ 0.0001; ns not significant