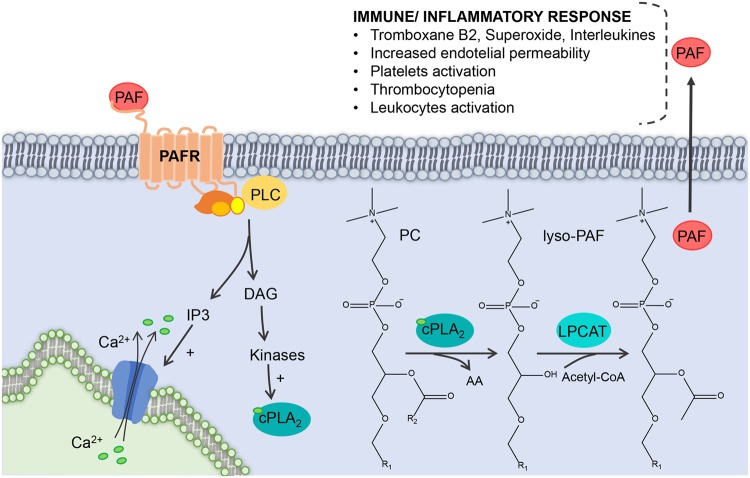
Figure 3.
The pool in the synthesis of PAFs that occurs under infection it is mediated by the activation of cPLA2, which recruits and hydrolyzes phosphatidylcholines for the formation of lysoPAF. The activation of cPLA2 due to extracellular stimuli (intracellular phosphorylation and Ca2+ influx) upon PAFs synthesis is initiated by the formation of lyso-PAF. Also, the action of the PAF acetylhydrolase, activated by Ca2+, and phosphorylation of lyso-PAF leads to PAF formation. PAF, Platelet activation factor; PAFR, Platelet activation factor receptor; PLC, Phospholipase; DAG, Diacylglycerol; IP3, Inositol trisphosphate; Ca2+, Calcium ions; cPLA2, Cytosolic phospholipase A2; PC, Phosphatidylcholine; AA, Arachidonic acid; Lysp-PAF, 1-O-alkyl-sn-glycer-3-phosphocholine; LPCAT, Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase; Acetyl-CoA, Acetyl coenzyme A.