Fig. 4.
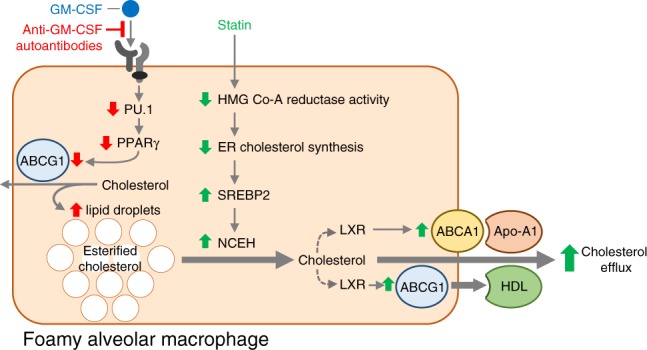
Proposed mechanisms for the pathogenesis and statin therapy of PAP. In the absence of GM-CSF signaling, surfactant-derived cholesterol accumulates progressively in lipid droplets resulting in foamy alveolar macrophages (red arrows indicate the effects of reduced GM-CSF signaling). Statin therapy results in increased cholesterol clearance from macrophages in PAP (green arrows represent the effects of statin in foamy alveolar macrophages)
