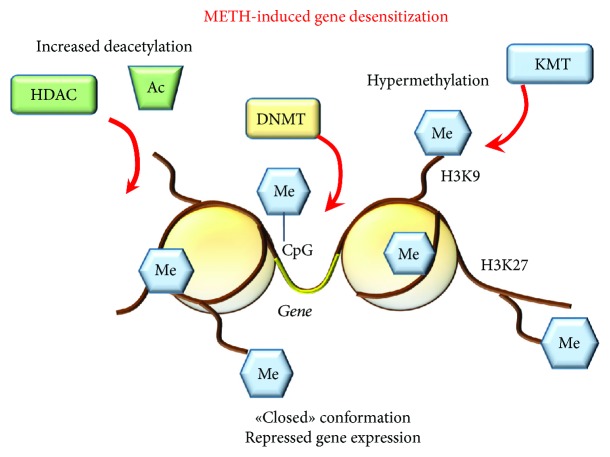
Figure 12.
METH-induced gene desensitization. Exposure to chronic METH produces epigenetic effects, which repress further gene expression. This occurs mainly through increased activity of deacetylation enzymes (HDAC), increased methylation of lysine 9 and 27 (K9/K27) residues of histones (i.e., H3K9/27) by methyltransferases (KMTs) and hypermethylation of gene promoters by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), which produce a “closed chromatin” conformation. Me: methyl groups; Ac: acetyl groups.