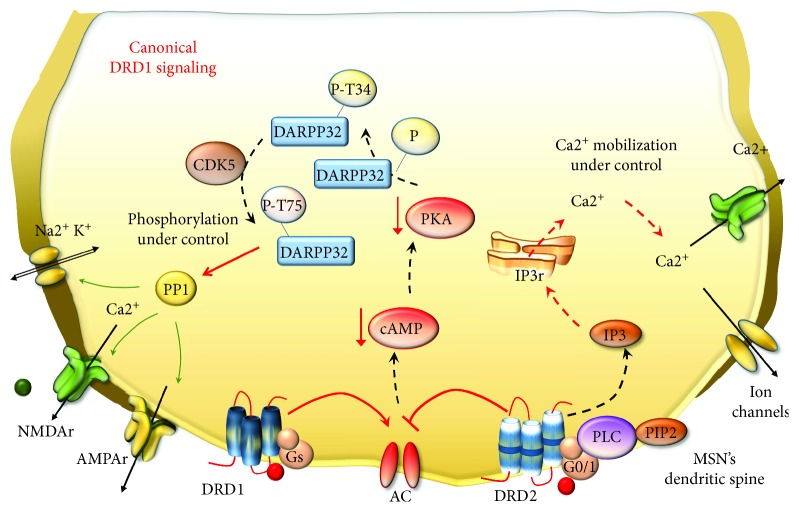
Figure 7.
An overview of canonical DA receptor signaling. During physiologic DA stimulation, AC activity is balanced by the excitatory and inhibitory effects of DRD1 and DRD2, respectively. Thus, there is a physiologic downregulation of cAMP and PKA activation. PKA has a broad array of targets such as the DA- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein (DARPP-32), voltage-gated ion channels, and GLUT receptors. PKA phosphorylates DARPP-32 at Thr34 (P-T34), but other proteins, such as cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5), counterbalance such an effect by phosphorylating DARPP-32 at a different site (P-T75). Thus, DARPP-32 can activate phosphatase protein 1 (PP1), which can surveil phosphorylation levels of all PKA targets. Likewise, canonical stimulation of DRD2, which are coupled with PLC, generates normal levels of inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate (IP3) which induces Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum. Since ion channels and GLUT receptors are properly functioning, intracellular Ca2+ can be efficiently mobilized.