Figure 1.
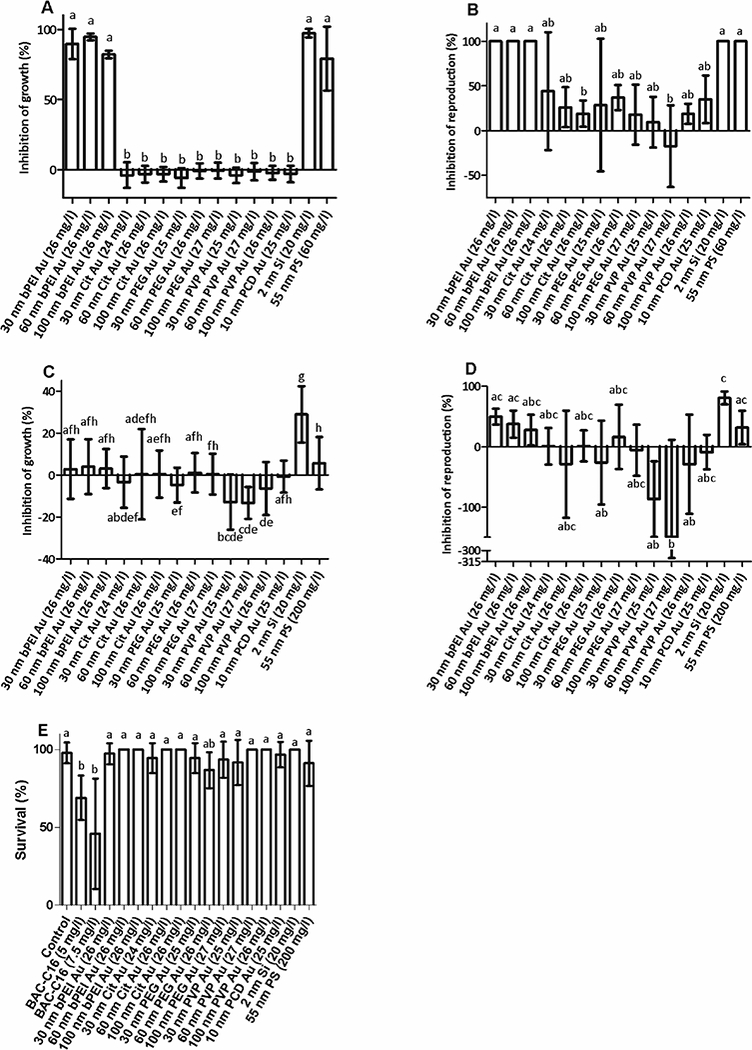
Toxicity of ENPs to C. elegans. A) Impacts of ENPs on growth and B) reproduction using ISO 10872 assay. Nematodes were exposed to ENPs for 96 h with E. coli as a food source in half-strength M9. For conditions where no juvenile worms were observed in any of the wells, error bars could not be included because there was 100 % reproduction inhibition for all replicates. C) Impacts of ENPs on growth and D) reproduction in axenic medium. Nematodes were exposed to ENPs for six days in an axenic nutrient medium to avoid interactions with E. coli. E) Impacts of ENPs on survival. Nematodes were exposed to ENPs for 24 h in M9 with no food or added nutrients present. Data are presented as mean inhibition of growth ± 1 standard deviation, n > 6 wells per ENP, each containing 10 adult nematodes for ISO and axenic assays. For the survival assay, n = 3 wells per ENP, each containing five nematodes. Bars with the same letter are not significantly different from one another; Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, p < 0.05.
