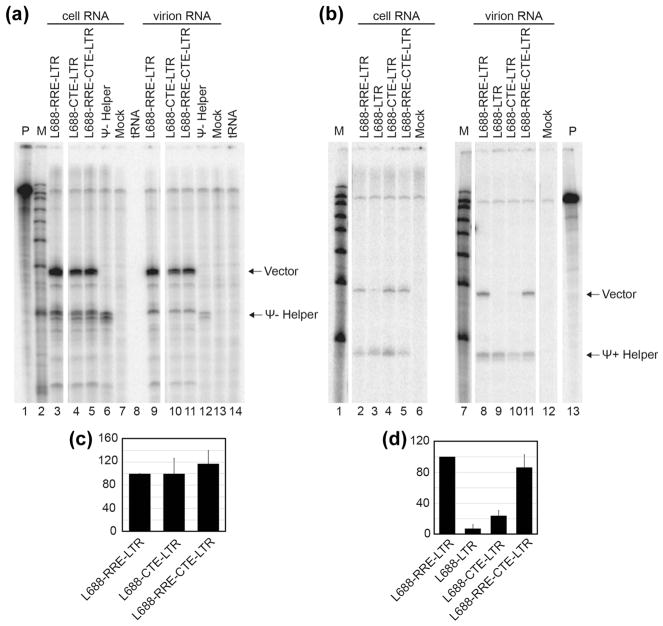
Figure 3.
Packaging efficiency of vectors containing a heterologous RNA transport element under non-competitive or competitive conditions. RNase protection assays were performed after co-expression of test vectors with Ψ− (A) or Ψ+ (B) helper. Riboprobe D (see Materials and Methods) was used in these experiments. Protected riboprobe fragments corresponding to test (Vector) and helper (Ψ− or Ψ+ Helper) RNAs are labeled. Lane designations indicate co-expressed HIV-1 vectors, markers, and controls as in Figure 2. (C) and (D) Quantification of packaging efficiency of HIV-1 vectors under non-competitive (C) or competitive (D) conditions. The packaging efficiency was calculated by dividing the ratio of vector RNA to helper RNA in virion samples by the ratio of vector RNA to helper RNA in the cells as determined by RNase protection analysis and quantified by phosphorimager analysis. The results present data from at least three independent experiments.