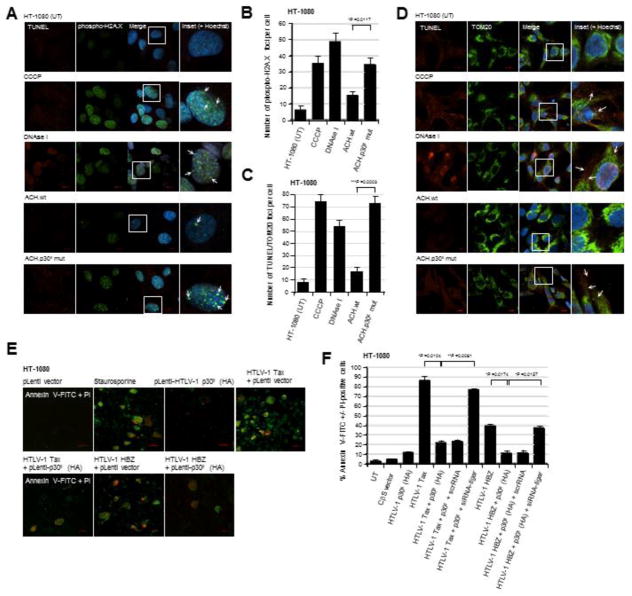
Fig. 3.
HT-1080 cells containing the infectious HTLV-1 ACH.p30II mutant provirus, defective for p30II production, exhibit increased genomic and mitochondrial DNA-damage as compared to the wildtype ACH provirus. (A and B) The parental HT-1080 cell-line and the HT1080/HTLV-1 ACH.wt and ACH.p30II mutant proviral clones were stained using a Click-iT Alexa Fluor 594-TUNEL kit (Molecular Probes; red signal) and a rabbit polyclonal primary antibody that recognizes the Ser139-phosphorylated histone variant H2A.X (Anti-Phospho-Ser139-H2A.X; green signal) which localizes at sites of genomic DNA-damage. The chemical uncoupler CCCP and DNAse I were included as positive controls. The cell nuclei were stained with the fluorescent dye, Hoechst 33342 (Molecular Probes; blue signal). The arrows in the enlarged inset panels at right indicate Phospho-Ser139-H2A.X foci in the merged images. The data in B represent the mean ± standard deviation (error bars) from three independent experiments. (C and D) HT-1080 cells and the HT-1080/HTLV-1 ACH.wt and ACH.p30II mutant proviral clones were stained using a fluorescent TUNEL kit (red signal) and a rabbit polyclonal Anti-TOM20 primary antibody (green signal) to detect mitochondrial DNA-damage resulting from oxidative stress. The cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342. Positive control samples were treated with either CCCP or DNAse I. The arrows in the enlarged inset panels at right indicate sites of mitochondrial DNA-damage. The graph in C shows the relative numbers of TUNEL/TOM20-positive foci per cell; and the data represent the mean ± standard deviation (error bars) from three independent experiments. (E and F) The ability of the HTLV-1 p30II protein to protect against Tax/HBZ-induced cytotoxicity was determined by either (E) transfecting HT-1080 cells with Tax or HBZ expression constructs and then transducing them with lentiviral-HTLV-1 p30II (HA) particles or an empty lentiviral vector, or (F) cotransfecting the cells with expression constructs for Tax, HBZ, and/or p30II (HA). Certain samples were repeatedly cotransfected with a siRNA-tigar oligonucleotide or scrRNA control using HiPerFect transfection reagent. The cells in E were also treated with staurosporine (100 nM) as a positive control to induce apoptosis. Apoptotic cells were detected by staining them with Annexin V-FITC (green signal) and propidium iodide (PI; red signal); and the relative percentages of Annexin V-FITC +/− PI-positive cells were quantified by fluorescence-microscopy, as compared to the total numbers of cells visualized using a DIC phase-contrast filter. All the data is representative of at least three independent experiments; and the data in F represent the mean of the experiments ± standard deviation (error bars).