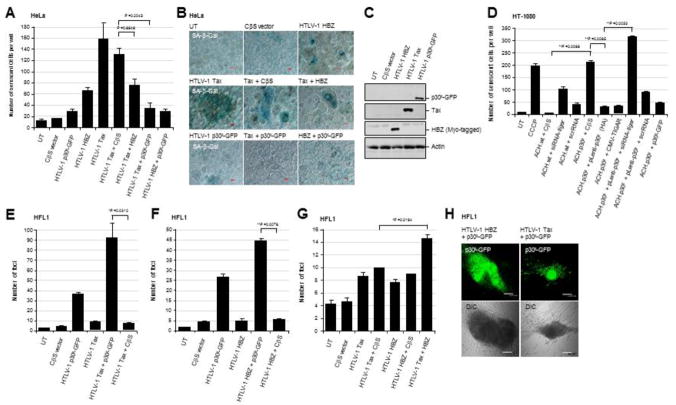
Fig. 4.
The HTLV-1 p30II protein inhibits Tax/HBZ-induced cellular senescence and cooperates with these major viral oncoproteins to induce oncogenic foci-formation in vitro. (A and B) To determine if p30II prevents Tax/HBZ-induced cellular senescence in HeLa cells as reported in Ho et al., 2012 and Kuo and Giam, 2006, the cells were cotransfected with an empty CβS vector or expression constructs for HTLV-1 Tax, HBZ, and/or p30II-GFP in various combinations. The cells were then cultured for five days and subsequently stained using an X-Gal solution to detect senescence-associated Beta-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) expression (blue signal in micrographs). DIC phase-contrast is included in the merged images for reference. The data in A represent the mean ± standard deviation (error bars) from three independent experiments. (C) The expression of the HTLV-1 Tax, p30II-GFP, and HBZ (Myc-tagged) proteins was detected by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. The relative levels of Actin are shown for comparison. (D) The parental HT-1080 cells and transiently-amplified HT-1080/HTLV-1 ACH.wt and ACH.p30II mutant proviral clones were cotransfected with an empty CβS vector, or expression constructs for HTLV-1 p30II-GFP or TIGAR (FLAG-tagged). Alternatively, the HT-1080/ACH.p30II mutant cells were transduced with lentiviral-HTLV-1 p30II (HA) particles or an empty pLenti vector. Certain samples were also repeatedly transfected with a siRNA-tigar oligonucleotide or scrRNA negative control. The cells were then stained with an X-Gal solution to detect SA-β-gal expression and analyzed by microscopy using a 20x objective lens to quantify the numbers of senescent cells per well. The data in D represent the mean ± standard deviation (error bars) from three independent experiments. (E-H) To determine whether the HTLV-1 p30II protein cooperates with the viral oncoproteins Tax and HBZ, the HFL1 human fibroblast cell-line (a pseudodiploid cell-line with a stable karyotype which grows as a uniform monolayer) was cotransfected with an empty CβS vector, or expression constructs for HTLV-1 Tax, HBZ, or p30II-GFP in various combinations. The stably transfected cells were monitored over a three-week period for the formation of oncogenically-transformed colonies (i.e., loss of contact-inhibition; see DIC phase-contrast images in H). The transformed colonies were fixed and stained with a methylene blue solution; and the numbers of transformed colonies per well were quantified by microscopy using a 10x objective. The expression of HTLV-1 p30II-GFP within transformed colonies was visualized by direct fluorescence-microscopy (top panels in H). The data in E, F, and G represent the mean ± standard deviation (error bars) from three independent experiments.