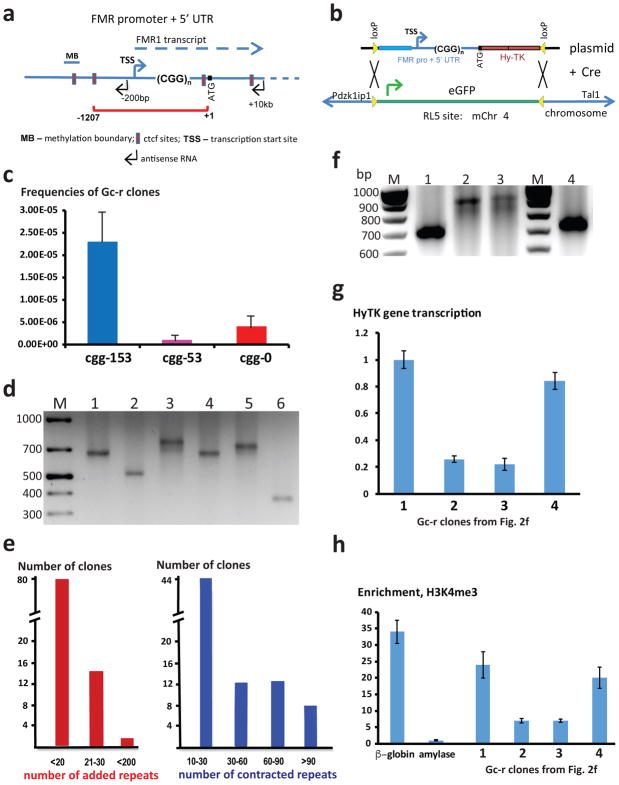
Figure 1. Experimental system to study genome instability caused by (CGG)n repeats.
a. FMR1 regulatory domain included in the selectable cassettes is shown by the red bracket; blue line represents human endogenous FMR 1 locus. b. FMR1-CGGn-HyTK cassettes were integrated into the RL5 locus in MEL cells via Cre-loxP recombination replacing the eGFP gene. A cassette can be integrated into the RL5 locus in two different orientations. c. Frequencies of Gc-r clones recovered. For clones with each experimental cassette, 96-well plates containing 106 cells were grown in the presence of ganciclovir, and Gc-r clones were counted. The number of analyzed plates were 17, 8 and 20 for CGG153-HyTK, CGG53-HyTK and CGG0-HyTK cassette, respectively. d. Sample PCR across the (CGG)153 run showing expanded (lanes 3 and 5), contracted (lanes 2 and 6) and unchanged repeats (lanes 1 and 4). e. Distribution of repeat expansions and contractions. f. PCR analysis of rare Gc-r clones containing large-scale repeats expansions (lanes 2–3); lane 1- starting repeat, lane 4 – small-scale expansion. g. qPCR analysis of the HyTK gene transcription in the clones shown in f. Means and standard deviations were calculated from three independent experiments. h. ChIP analysis of the H3K4me3 chromatin mark in the clones shown in f. The murine beta-major globin and the murine amylase genes were used as controls for open and condensed chromatin, respectively. Means and standard deviations were calculated from three independent experiments. Source data for d and f are available online.