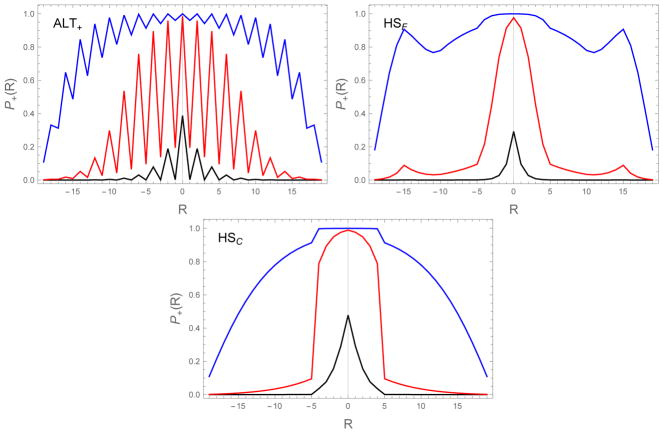
Figure 8.
Capture probabilities (Eq. (18)) as a function of binding alignment R and the diffusion collision rate ron=104 s−1 (black), 106 s−1 (red), to 108 s−1 (blue). Higher values of ron, corresponding to higher monomer concentration, result in greater probability for mis-registered molecules to be incorporated in the fibril. The HP sequences show considerably more structure than the exponential dependence of the UNI sequence (Figure 3) due to the effects of aligning the strong binding H residues. In particular, the ALT sequence has lower capture probabilities when R is odd because these alignments only allow for the formation of weak H-P bonds. Also, the HSF sequence shows secondary peaks at large |R| when the H residues from opposite ends of the chain are brought together. ε0 = 0.5, δ = 0.3