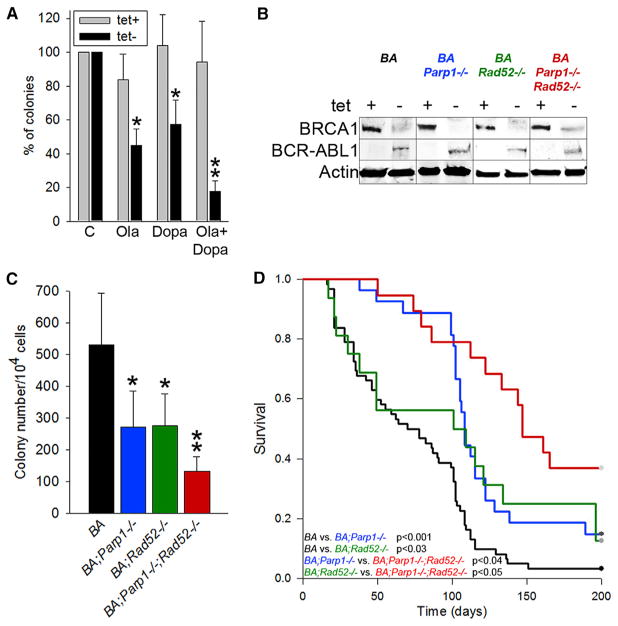
Figure 4. The Effect of Simultaneous Inactivation of RAD52 and PARP1 on Leukemo-genesis in BRCA1-Deficient BCR-ABL1 Transgenic Mice.
(A) Sensitivity of clonogenic bone marrow cells from SCLtTA;p210BCR-ABL1 mice (n = 3) to 5 μM olaparib (Ola) and/or 20 μM 6-OH-dopa (Dopa) in the absence of tetracycline. Results represent mean percentage of clonogenic cells ± SD from three mice in triplicates; *p < 0.001 in comparison with untreated cells using Student’s t test; **p = 0.016 compared with individual drugs using the response additivity approach.
(B–D) SCLtTA;p210BCR-ABL1;Parp1−/−; Rad52−/− (BA;Parp1−/−;Rad52−/−), SCLtTA;p210 BCR-ABL1;Parp1−/− (BA;Parp1−/−), SCLtTA; p210BCR-ABL1;Rad52−/− (BA;Rad52−/−), and SCLtTA;p210BCR-ABL1 (BA) mice were assayed for (B) expression of BRCA1, BCR-ABL1, and actin proteins in the absence (−) or presence (+) of tetracycline; (C) clonogenic activity of bone marrow cells from BA;Parp1−/−;Rad52−/−, BA; Parp1−/−, BA;Rad52−/−, and BA mice (at least three mice per group) (results show mean ± SD number of BCR-ABL1-dependent colonies [tet− – tet+]; *p < 0.02 compared with BA and **p < 0.05 compared with BA;Parp1−/− and BA;Rad52−/−); and (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of BA;Parp1−/−;Rad52−/− (n = 19), BA;Parp1−/− (n = 27), BA;Rad52−/− (n = 16), and BA (n = 63) mice.
See also Figure S4.