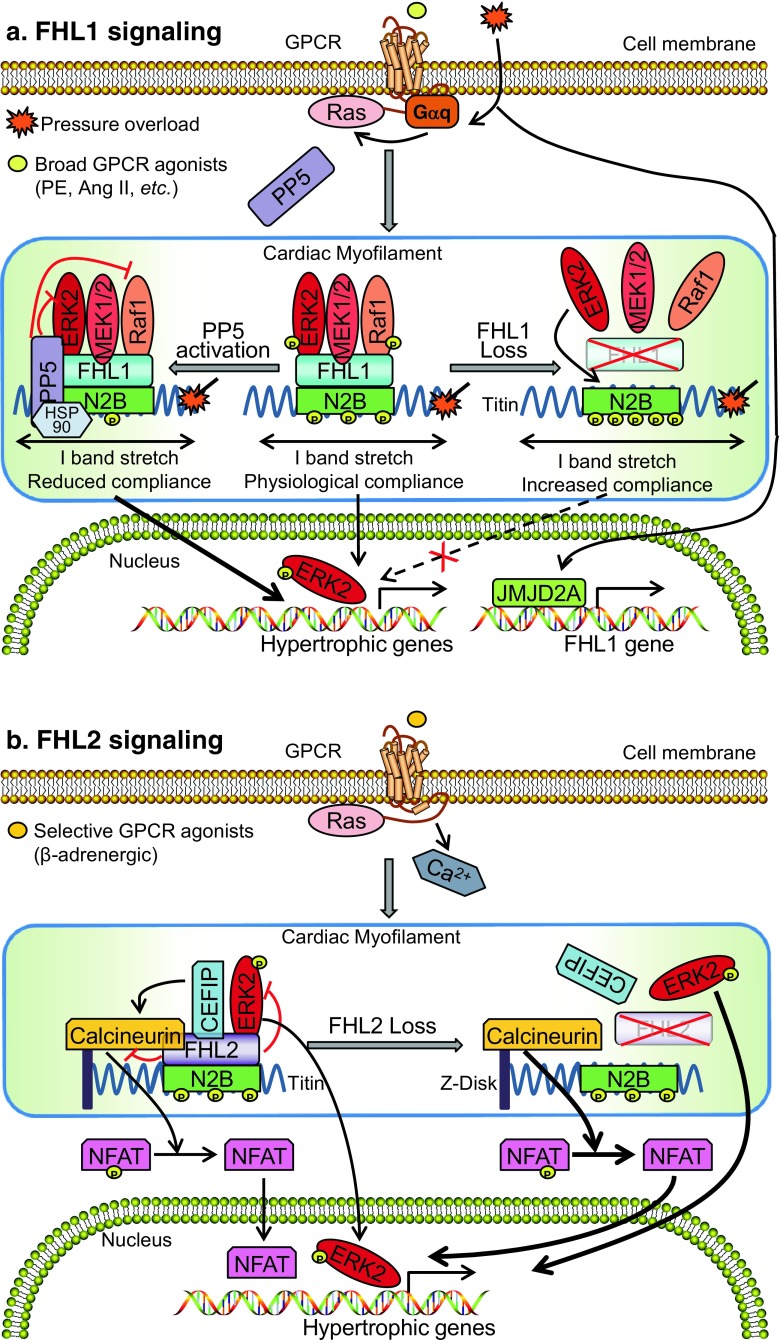
Fig. 1.
Schemata of the signaling pathways underlying a role for FHL1 and FHL2 in cardiac hypertrophy. a FHL1 scaffolds MAPK components (Raf-1/MEK2/ERK2) to the sarcomeric titin N2B spring element (biomechanical stress sensor complex), to transmit MAPK signals to regulate muscle compliance and cardiac hypertrophy in a Gq stimulus-specific manner. Loss of FHL1 dissociates this biomechanical stress sensor complex and unmasks phosphorylation sites at titin N2B by ERK2, resulting in increased muscle compliance and a blunted response upon hypertrophic stimulus. PP5 translocates and deactivates this biomechanical stress sensor complex, leading to decreased muscle compliance and heart failure. b FHL2 interacts with EKR2, CEFIP, and calcineurin at the sarcomere to suppress MAPK/ERK and calcineurin/NFAT signaling upon adrenergic-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Loss of FHL2 releases the suppression of the MAPK/ERK and calcineurin/NFAT signaling, leading to increased cardiac hypertrophy. Ang II, angiotensin II; CEFIP, cardiac-enriched FHL2-interacting protein; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FHL1, four and a half LIM domain protein-1; FHL2, four and a half LIM domain protein-2; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor; HSP90, heat shock protein 90; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; PE, phenylephrine; PP5, protein phosphatase 5