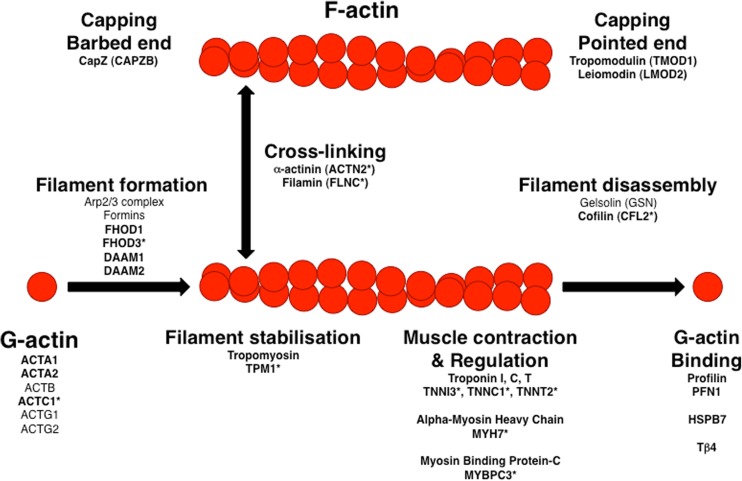
Fig. 1.
Overview of actin-binding proteins and their effect on actin. Actin-binding proteins can enhance the formation of filaments from G-actin monomers, can stabilise and crosslink these filaments and can also disassemble them. The end of the filaments are termed barbed (plus end) and pointed (minus end) and dissociation of G-actin is prevented by different capping proteins. Disassembly of actin filaments is favoured by members of the gelsolin family. Gene names are given below the roles; names in bold are highly expressed in cardiomyocytes. An asterisk after the name indicates that these genes were shown to bear mutations that can cause hereditary cardiomyopathy