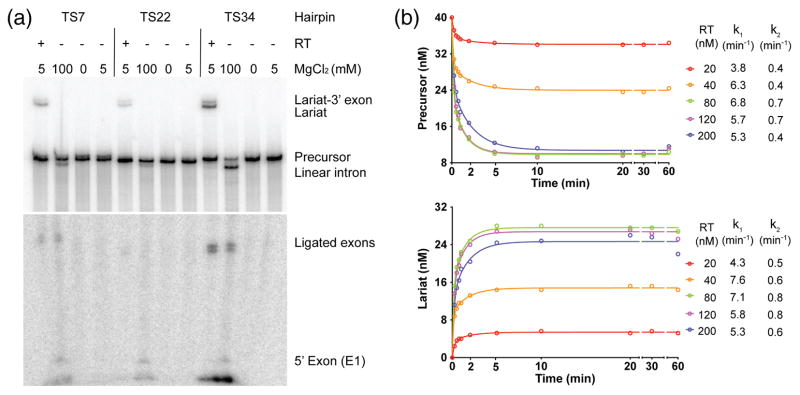
Fig. 7.
Protein-dependent and self-splicing of GsI-IIC. (a) Protein-dependent and self-splicing reactions of GsI-IIC from precursor RNAs with different 5′ exons. 32P-labeled precursor RNAs (10 nM) were incubated with GsI-IIC RT (20 nM) for 10 min at 50 °C in reaction medium containing 5 mM Mg2+ (protein-dependent splicing conditons), without protein in reaction medium containing 100 mM Mg2+ (self-splicing conditions), no Mg2+ (non-splicing control), or 5 mM Mg2+ (5 mM; control for self-splicing under protein-dependent splicing conditions). Bands are identified to the right of the gel. The gel is split to show differently exposed top and bottom portions. (b) Time courses of the protein-dependent splicing reaction. 40 nM GsI-IIC RNA was incubated with various amounts of purified GsI-IIC RT (20 to 200 nM, color coded as indicated to the right). Samples were taken at different times, and the products were analyzed in a denaturing 4% polyacrylamide gel, which was dried and scanned with a Phosphorimager. The sets of curves at the top and bottom show disappearence of precursor RNA and appearance of intron lariat RNA, respectively. k1 and k2 indicate the fast and slow rate constants obtained from fitting the data to an equation with two exponentials using Prism6 (GraphPad Software).