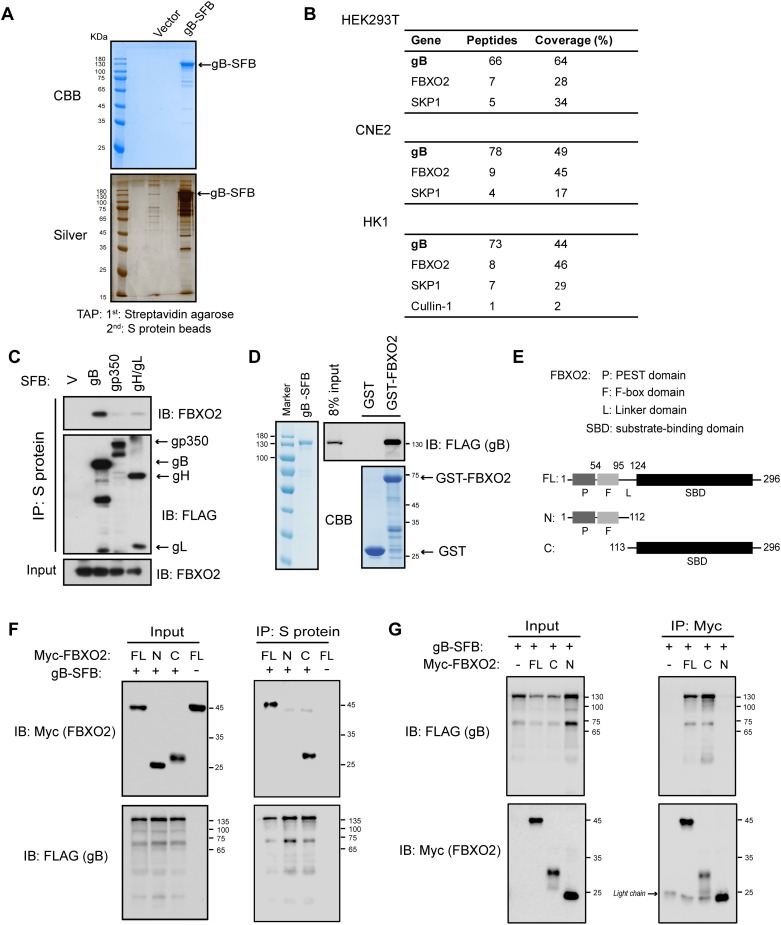
Fig 1. FBXO2 binds to gB via its substrate/sugar-binding domain.
(A) TAP of C-terminal SFB-tagged gB in HEK293T cells. Final eluted proteins were analyzed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB; top) or silver staining (bottom). (B) Summary of proteins identified by TAP-MS analysis in HEK293T, CNE2 and HK1 cell lines stably expressing gB-SFB. (C) HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding SFB-tagged gB, gp350, gH/gL or empty vector. Cell lysates were subjected to precipitation using S-protein beads, and the bound protein was determined by Western blotting (WB). (D) Direct binding of gB to FBXO2. Bacterially purified GST-FBXO2 or GST alone was incubated with gB purified from stably infected HEK293T cells. Proteins bound to glutathione Sepharose beads were analyzed by WB. (E) Schematic representation of the FBXO2 domain structure. P, PEST domain; F, F-box domain; SBD, substrate-binding domain; FL, full-length. (F) Co-IP of FBXO2 fragments and gB. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with plasmids encoding Myc-tagged FL FBXO2 or N- or C-terminal FBXO2 fragments and gB-SFB. Cell lysates were precipitated with S-protein beads and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (G) Reciprocal co-IP of gB and FBXO2 fragments. The procedures were similar to those performed in (E) except that the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc agarose. The arrowhead indicates IgG light chain. The sizes of molecular mass markers (M) are shown in kDa.