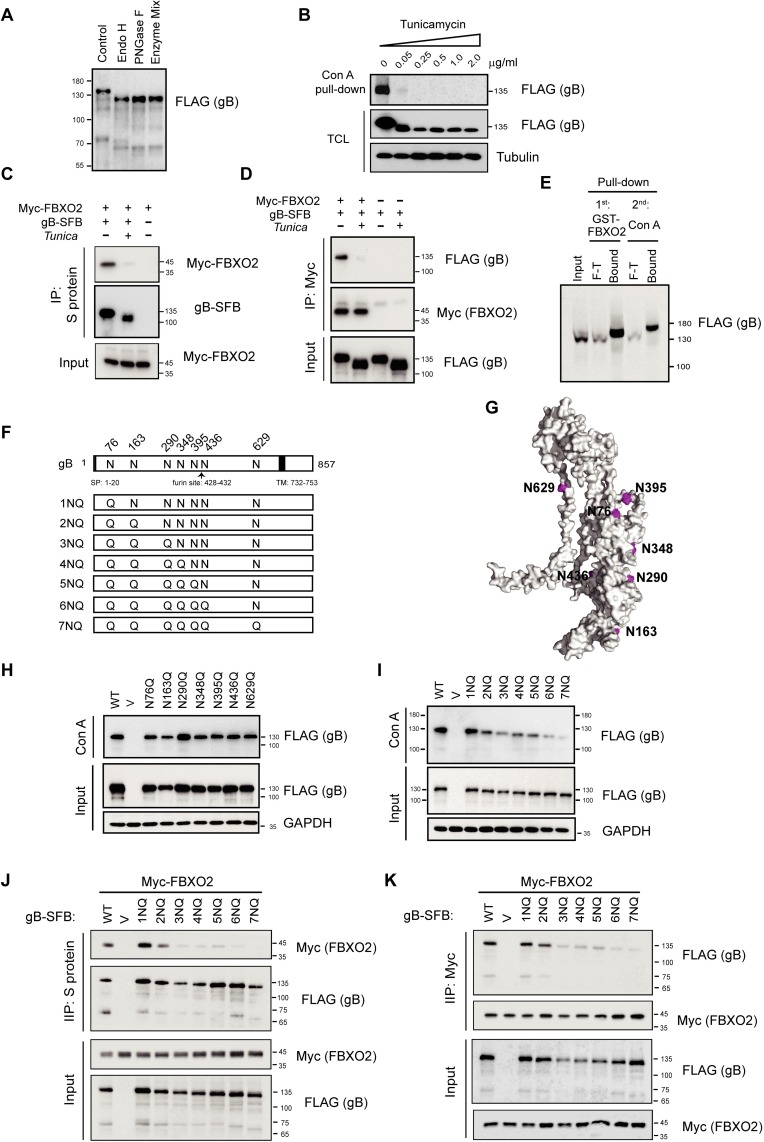
Fig 3. N-linked high-mannose glycosylation of EBV gB is required for FBXO2 interaction.
(A) Analysis of glycan modifications of gB. gB-SFB purified from CNE2 cells stably expressing the protein was treated with endoglycosidase H (Endo H) or PNGase H or a Deglycosylation Mix before electrophoresis on 8% polyacrylamide gels. The sizes of molecular mass markers (M) are shown in kDa. (B) CNE2 cells stably expressing gB-SFB were treated with tunicamycin at different concentrations as indicated overnight before harvest. Con A agarose was used to enrich N-linked glycoproteins. TCL: total cell lysates. (C-D) Inhibition of N-linked glycosylation of gB by tunicamycin abrogates the gB-FBXO2 association. HEK293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding Myc-FBXO2 and gB-SFB were treated with 0.25 μg/mL tunicamycin or DMSO for 24 h, and the cells were harvested and subjected to immunoprecipitation by S-protein agarose (C) or anti-Myc agarose (D). (E) Sequential pull-down of glycosylated gB by GST-FBXO2 followed by Con A agarose pull-down. Eight percent of the TCL of cells stably expressing gB was loaded as input; F-T: 8% of the flow-through. (F) Schematic diagram of glycosylation sites on gB and its N-to-Q mutants. The signal peptide (SP), furin cleavage site and transmembrane (TM) domain of gB are indicated. (G) Ribbon diagrams of the monomeric EBV gB structure, illustrated with the PyMol program using PDB 3FVC as the template. The glycosylation sites as shown in (F) are colored in magenta. (H-I) Con A agarose pull-down of gB single (H) or multiple (I) N-to-Q mutants. (J-K) Co-IP of FBXO2 with glycosylation-defective gB mutants. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with Myc-FBXO2 and gB N-to-Q mutants as indicated, and the cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation by S-protein agarose (J) or anti-Myc agarose (K) and immunoblotted with anti-Myc and anti-FLAG antibodies.