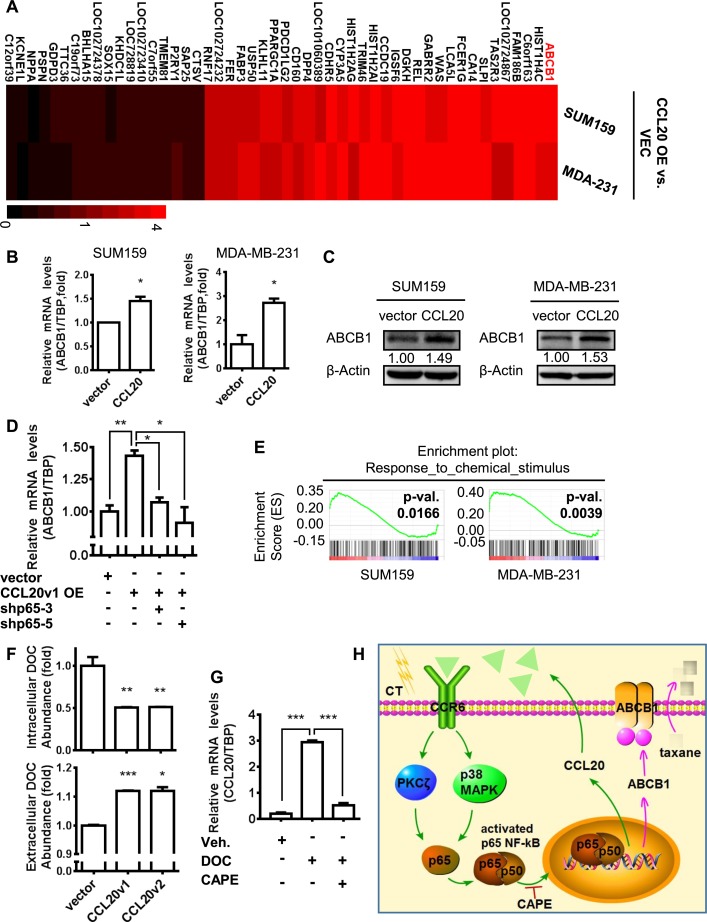
Fig 6. ABCB1 up-regulation mediated by CCL20-induced NF-κB activation reduced the intracellular abundance of taxane and promoted chemoresistance in breast cancer cells.
(A) Transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) utilizing the next-generation technology was conducted with RNA from vector (“VEC”) and CCL20v1-overexpressing (“CCL20 OE”) SUM159 cells and MDA-MB-231 cells. Heat map shows expression levels of the most up-regulated genes (>1.5-fold) and significantly down-regulated genes (decline more than 40%) both in CCL20v1-overexpressing cells of SUM159 and MDA-MB-231 versus vector. Values are the fold change to vector. (B-C) The mRNA and protein levels of ABCB1 were determined by qRT-PCR or western blot in vector and CCL20v1-overexpressed cells of SUM159 and MDA-MB-231. (D) Level of ABCB1 was determined by qRT-PCR in MDA-MB-231 cells. (E) Pathway of response to chemical stimulus was positively correlated with CCL20 overexpression in GSEA from RNA-seq in (A). Nominal P value was shown. (F) Vector and CCL20-overexpressing MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 200 nM DOC for 12 hours. Then, supernatants and cells were collected for quantitative analysis of DOC abundance with HPLC-MS. (G) MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of DOC (10 nM) or CAPE (5 μM); then, the mRNA level of CCL20 was determined by qRT-PCR. (H) A cartoon to illustrate the pattern of CCL20-induced NF-κB activation through PKCζ or p38 MAPK pathway to up-regulate expression of ABCB1 for taxane pumping-out, leading to chemoresistance. Data are shown as mean ± SEM and are representative of 3 independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by unpaired t test of triplicates. ABCB1, ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1; CAPE, caffeic acid phenethyl ester; CCL20, C-C motif chemokine ligand 20; CCR6, C-C motif chemokine receptor type 6; DOC, docetaxel; GSEEA, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis; HPLC-MS, high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; PKCζ, protein kinase Cζ; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR; RNA-seq, RNA sequencing; TBP, TATA-box binding protein.