Fig. 4. TLK depletion causes genomic instability and sensitizes cells to checkpoint inactivation and PARP inhibition.
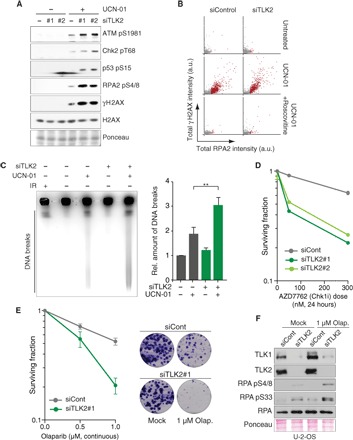
(A) Analysis of DNA damage signaling in U-2-OS cells 24 hours after siRNA transfection and treatment with or without UCN-01 for 2 hours. One representative experiment of three biological replicates is shown. (B) HTM analysis of RPA accumulation and γH2AX in TLK2-depleted U-2-OS cells treated with UCN-01 alone or together with roscovitine for 2 hours. One representative experiment of two biological replicates is shown (n > 1800). (C) PFGE analysis of DNA DSBs in U-2-OS cells transfected with siRNAs for 24 hours and treated with UCN-01 for 4 hours. Representative result (left) and quantification (right) of DNA breaks relative to untreated control from n = 3 independent experiments are shown with the means and SD. An unpaired two-tailed t test was used for statistical analysis. **P < 0.01. IR, ionizing radiation, 20 Gy. (D) Sensitivity of TLK-depleted cells to the CHK1 inhibitor AZD7762 measured by colony formation assay. Representative experiment of two biological replicates performed in technical duplicate is shown. (E) Sensitivity to PARP inhibitor olaparib measured by colony formation assay; representative images are shown. Means and range of two biological replicates performed in technical duplicate are shown. (F) Western blotting of RPA and phospho-RPA following TLK depletion and olaparib treatment in U-2-OS cells.
