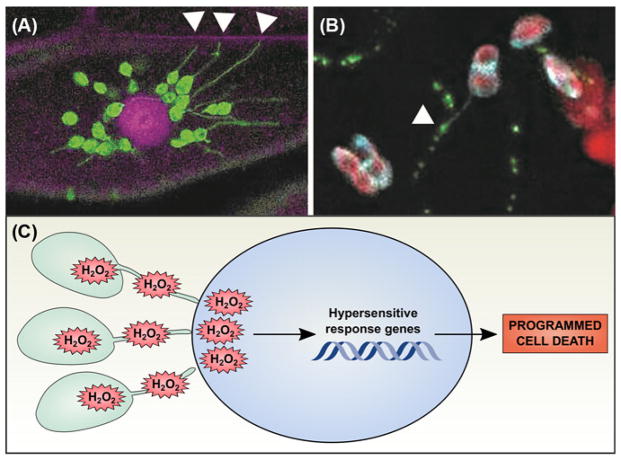
Figure 4. Stromules may participate in chloroplast signaling pathways.
(A) Chloroplast stromal GFP (green) reveals the presence of stromules, stroma-filled tubular extensions from the main body of the chloroplast. Here, chloroplasts are surrounding the nucleus (stained with propidium iodide, magenta) and extending stromules to the cell wall (also stained with propidium iodide, magenta; stromules associated with the cell wall indicated with white arrowheads). (B) Stromules are occasionally observed in close physical association with plasmodesmata. Tobacco mosaic virus movement protein P30 was fluorescently tagged with GFP (green) and transiently expressed in a transgenic N. benthamiana line expressing a chloroplast stromal Cerulean marker (cyan); chlorophyll autofluorescence is also shown (red). An example of a stromule extending from a chloroplast to associate with a PD (marked with P30-GFP) is indicated with a white arrowhead. Images were obtained by the authors with a Zeiss LSM 710 confocal scanning laser microscope. (C) During the hypersensitive response, chloroplasts generate large quantities of H2O2 that can travel through stromules to be released in the nucleus. High levels of H2O2 then promote the hypersensitive response genetic program, leading to programmed cell death.