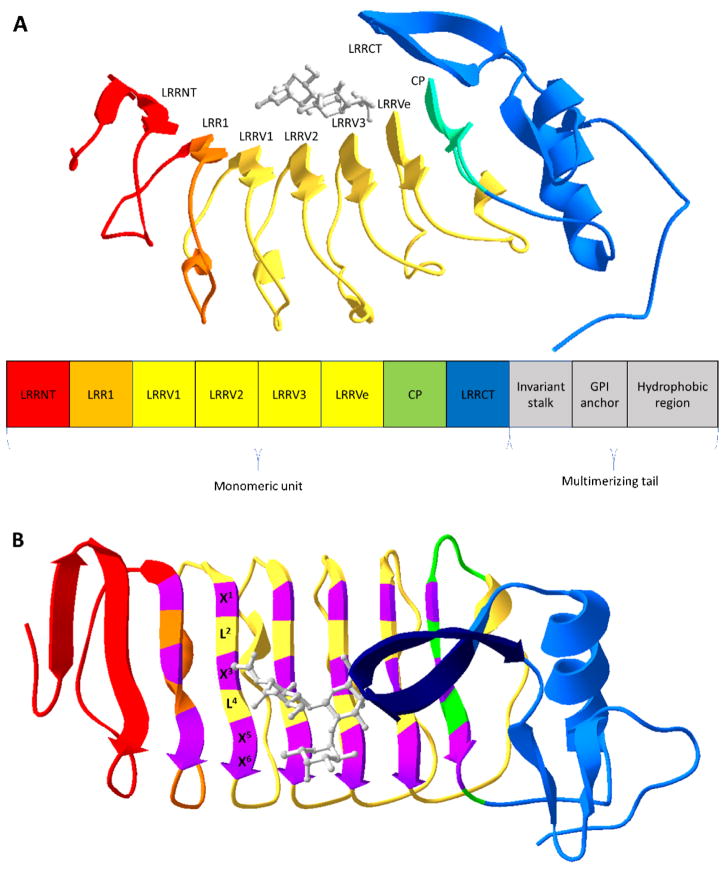
Figure 1.
Overview of VLR structure. (A) Ribbon structure of a monomeric VLR in complex with an H-trisaccharide (gray) (PDB code 326J [16]). Below the ribbon structure is a modular rendition of a full-length VLR consisting an N-terminal cap (LRRNT), the first leucine-rich repeat (LRR) module (LRR1), three variable LRR (LRRVs), an end variable LRR (LRRVe), a connecting peptide (CP), a C-terminal cap (LRRCT), an invariant stalk, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor, and a hydrophobic region. (B) The VLR structure is rotated 90° with highly variable residues of the 6-residue motif (X1LX3LX5X6) in purple and the variable sized insert of the LRRCT in dark blue. X represents highly variable amino acids and L, leucine.