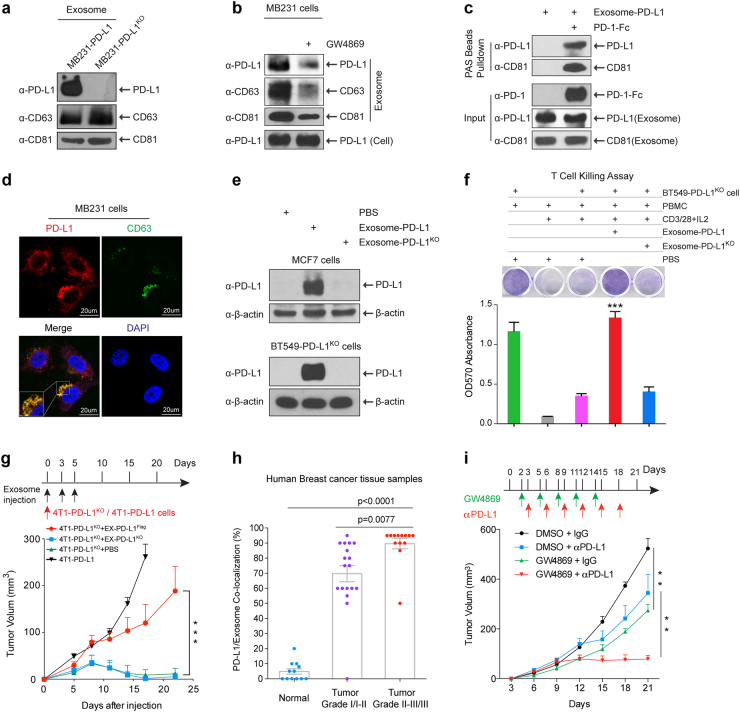
Fig. 1.
PD-L1 existed in exosomes and played important roles in breast tumor growth. a Western blot of PD-L1 in exosomes isolated from the media of 231-PD-L1 and 231-PD-L1KO cells with the indicated antibodies. CD63 and CD81, exosome markers. b Western blot of PD-L1, CD63, CD81 in exosomes isolated from 231-PD-L1 cells with or without GW4869 (10 μM) treatment for 48 h with the indicated antibodies. c PD-L1-containing exosome were incubated with PD-1-Fc recombinant proteins followed with protein A sepharose pulldown. PD-L1 and CD81 were detected by Western blotting. One percent of PD-1-Fc proteins and exosome-PD-L1 served as input. d Confocal microscopy of PD-L1 (red) and CD63 (green) in 231 breast cancer cells. Yellow, co-localization of PD-L1 and CD63 in MVBs. e Exosome-PD-L1, exosome-PD-L1KO, or PBS was added to MCF7 (PD-L1 low) or BT549-PD-L1KO cells. After 24-h incubation, cells were washed with PBS 4 times, lysed in lysis buffer, and subjected to Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. f Top, T-cell-meditated tumor cell-killing assay in BT549-PD-L1KO cells incubated with exosome-PD-L1, exosome-PD-L1KO, or PBS. Bottom, quantification of cell viability. g Tumor growth of PD-L1 deficient 4T1 cells (4T1-PD-L1KO) in BALB/c mice injected with EX-PD-L1Flag or EX-PD-L1KO as indicated. Tumor volume was measured at the indicated time points (n = 10 mice per group). h Co-localization analysis of PD-L1 and exosomes in human breast cancer tissue microarray. Samples were double stained with PD-L1 and CD63 antibody. The percentage of PD-L1 and CD63 co-localization was determined by the green/brown color as described in Supplementary information, Figure S1e. i Tumor growth of 4T1 cells in BALB/c mice treated with GW4869 and/or PD-L1 antibody. Tumor volume was measured at the indicated time points (n = 8 mice per group). Data represent mean ± SEM, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 or as indicated, Student’s t-test