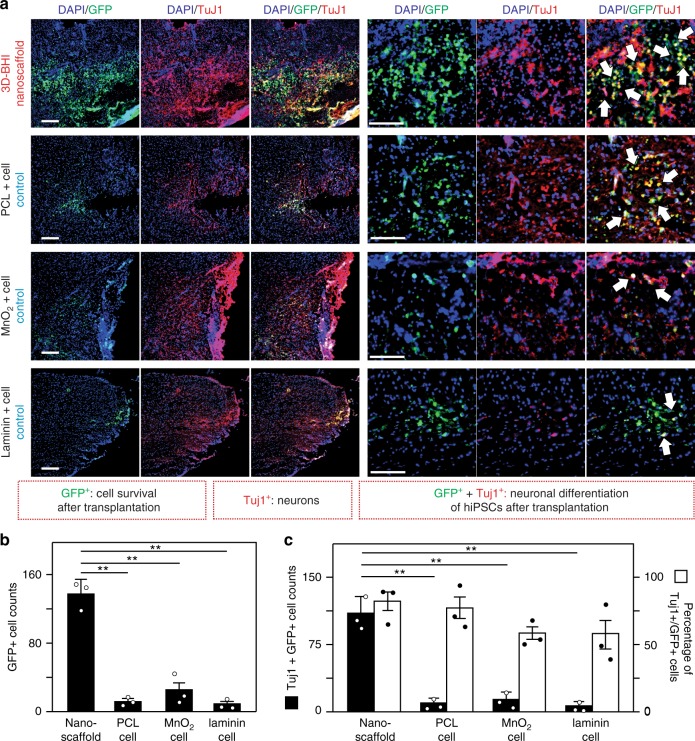
Fig. 7.
3D-BHI nanoscaffold enhances survival and neuronal differentiation of hiPSC-NSC-GFP. a Immunohistological staining analysis was performed on tissue slices from 4 different animal groups transplanted with hiPSC-NSC-GFP to determine enhanced cell survival and improved neurogenesis from our 3D-BHI nanoscaffold transplanted condition. All tissue analysis was performed 1-week post transplantation and stained with DAPI (blue) and TuJ1 antibodies (red). Arrows indicate neuronal cells differentiated from hiPSC-NSC-GFP (identified by TuJ1+/GFP+ cells). b By quantifying the number of remaining GFP+ cells, the ability of 3D-BHI nanoscaffold to retain the significant higher amount of cells after transplantation was demonstrated by comparing to other cell transplantation groups. c Improved cell transplantation by our nanoscaffold can be further evidenced by an increased neuronal cell population and a higher percentage of neuronal cells in GFP+ cells (area = 1 mm2). This is consistent with Supplementary Fig. 20, where co-labeling of GFP+/TuJ1+ and GFP+/GFAP+ nearby the injured sites suggest most of the transplanted hiPSC-NSC-GFP become neuronal cells but not astroglial cells. Scale bars: 100 μm. Error bars represent mean ± s.d.; n = 3, **P < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc test