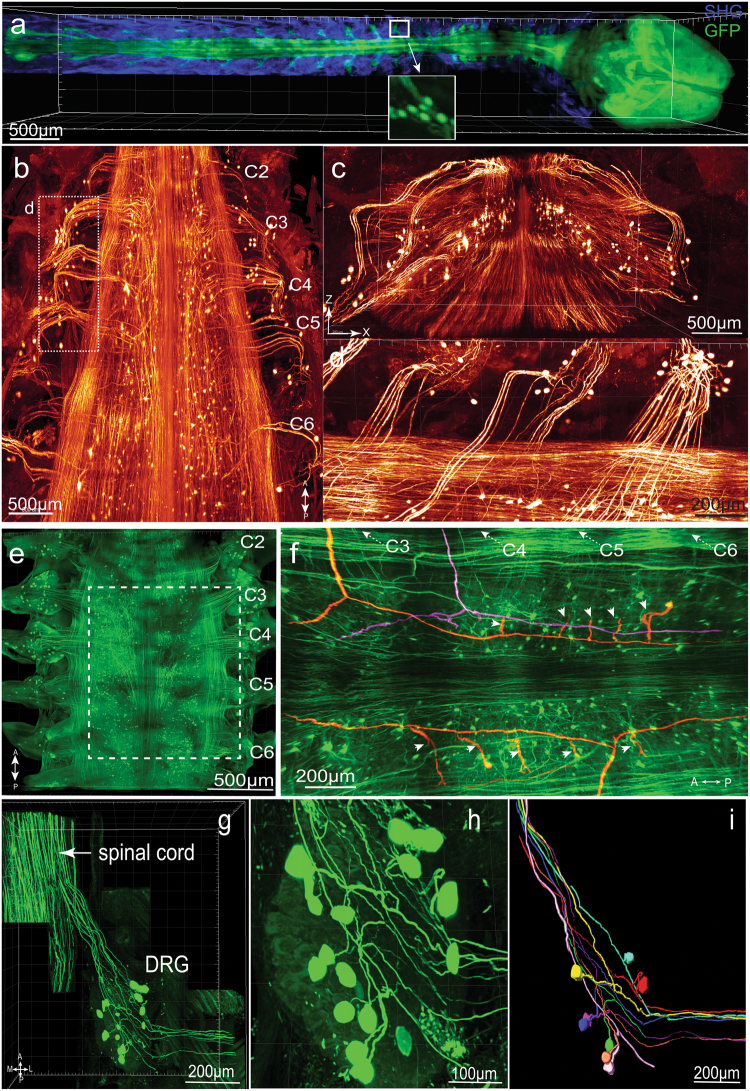
Fig. 8.
PEGASOS enables visualization of connections between CNS and PNS by imaging through the vertebrae. Adult Thy1-EGFP mice (2-months-old) were cleared following PEGASOS recirculation procedure and the vertebrae and brain were dissected for imaging. a The intact CNS together with DRGs were imaged with a 5×/0.16 objective on a two-photon microscope. Boxed area is enlarged in the insert to show individual DRG neurons. b A segment of cervical vertebrae (C2–C6) was imaged with a 1× 0.25NA objective on a tiling light-sheet microscope. X-Z optical slice was shown in c to display the cross section of the spinal cord. Boxed area in b was enlarged in d to display DRG neurons and their central axons. e A segment of the cervical vertebrae (C2–C6) was imaged with a 10×/0.45 objective on a confocal microscope to visualize cervical DRGs. f Optical sections were acquired at boxed region in e. Individual central axons were labeled. Each central axon (highlighted with color) gives rise to two daughter branches and then to multiple collateral branches (arrowheads). The entire tracing length is over 2 cm. g–i The C4 DRG was re-imaged with a 20×/0.95 objective to reveal connections between DRG neurons and the spinal cord. h Enlarged view shows individual DRG neurons within the C4 DRG. i Eight pseudo-unipolar neurons were individually identified and artificially labeled with different colors. SHG second harmonic generation signal. A, anterior; P, posterior; L, lateral; M, medial