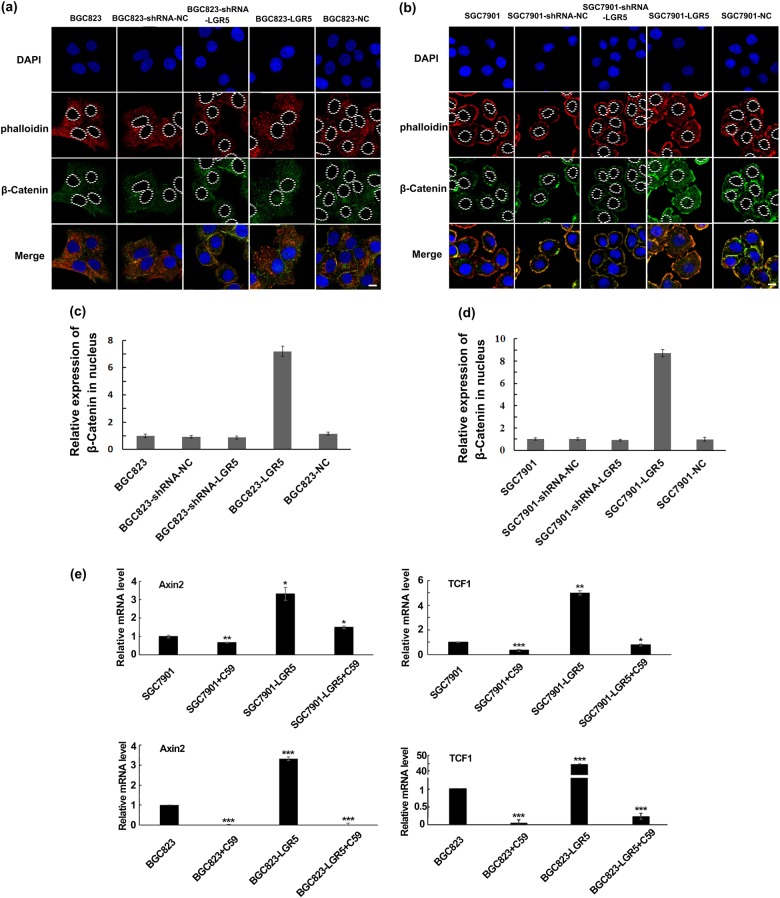
Fig. 6. LGR5 regulates expression and location of β-catenin and expression of Wnt/β-catenin target genes in BGC823 and SGC7901 cells.
a, b BGC823 and SGC7901 cells were treated with corresponding vectors. Seventy-two hours after transfection, the cells were subjected to immunofluorescent staining for β-catenin (green) and phalloidin staining (red). Nuclei were visualized with DAPI (blue). In control cells (BGC823, BGC823-shRNA-NC and BCG823-NC; SGC7901, SGC7901-shRNA-NC, and SGC7901-NC), β-catenin was with moderate staining distributed in the cytoplasm. When LGR5 was overexpressed, β-catenin staining was increased in cytoplasm and translocated to the nucleus in BCG823 cells. Depleting LGR5 reduced β-catenin level in nucleus and cytoplasm. Scale bar = 10 μm. c, d The relative expression level of β-catenin in nucleus in each group was examined by average fluorescence intensity, and the results are presented graphically as mean ± SD of three independent measurements. **P < 0.01. e Two Wnt/β-catenin target genes were chosen to investigate whether Wnt pathway is activated by LGR5. Axin2 and TCF1 mRNA expression levels in SGC7901 and BGC823 cells treated with or without 10 μM C59 were detected. The graph presented mean ± SD of three separate samples for each cell type, each normalized to parental cells. Significance levels were determined by the unpaired t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by t test; n = 3