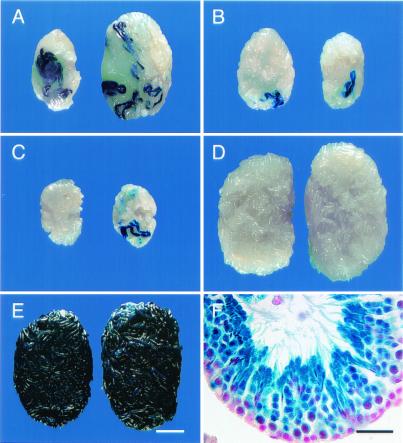
Figure 1.
Macroscopic and histological appearance of W and wild-type B6/129-recipient testes that were injected with spermatogonial stem cells transduced by a retroviral vector containing a lacZ reporter gene. (A) Testes of W male 5483 that was fertile and produced transgenic progeny (killed at 379 days). Note size of testes, number of blue colonies, and total blue area. (B) Testes of W male 5654 that was fertile but produced no transgenic progeny (killed at 319 days). Note size of testes and small number of blue colonies. (C) Testes of W male 5485 that was not fertile (killed at 307 days). Testes are small; total weight is ≈40% of A and 53% of B. (D) Testes of wild-type B6/129 male 5650 (killed at 273 days). Note normal size and absence of blue colonies. (E) Testes of 5486-4 progeny of W male 5486 (killed at 320 days). Testes are normal size and all tubules stain blue. (F) Histological section of seminiferous tubule from testes of W male 5486. Note normal organization of spermatogenesis and production of spermatozoa from stem cell transduced by vector. All germ cells carry the transgene and stain blue. Right testes appear on Right in A–E. Stain: A–F, 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl β-d-galactosidase (X-gal); F, nuclear fast red counterstain. [Bars = 2 mm (A–E) and 30 μm (F).]