Figure 4.
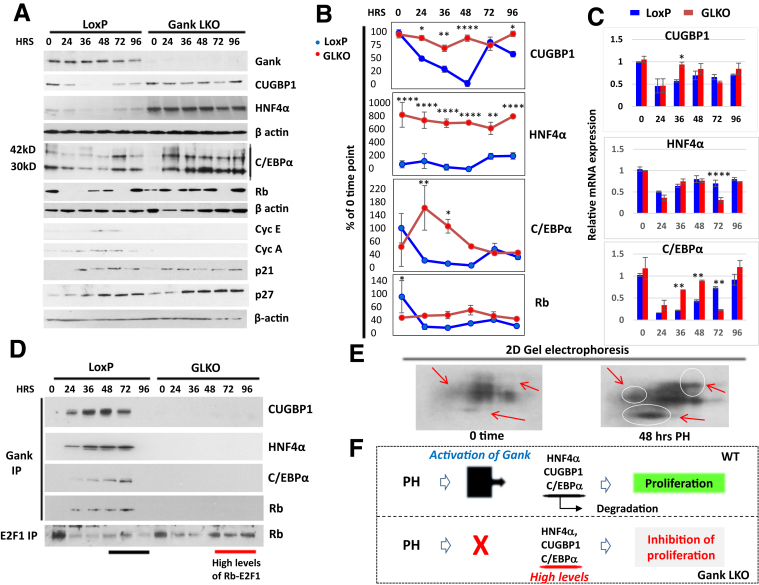
The inhibition of liver proliferation in Gank LKO mice is mediated by high levels of tumor-suppressor proteins. (A) Western blot analysis of nuclear extracts for expression of proteins (right) in livers of LoxP and Gank LKO mice after PH. C/EBPα is expressed as 2 isoforms with a molecular weight of 42 and 30 kilodaltons. All Western blots of TSPs had 2 biological replicates and 1–2 technical replicates. (B) Calculations of levels of TSPs as ratios to β-actin. Statistical analysis was performed with biological replicates. P values for CUGBP1 were as follows: 0 hours (P > .99), 24 hours (P < .03), 36 hours (P < .01), 48 hours (P < .0001), 72 hours (P > .99), and 96 hours (P < .03). P values for HNF4α were as follows: 0 hours (P < .0001), 24 hours (P < .0001), 36 hours (P < .0001), 48 hours (P < .0001), 72 hours (P < .0019), and 96 hours (P < .0001). P values for C/EBPα were as follows: 0 hours (P > .13), 24 hours (P < .001), 36 hours (P < .02), 48 hours (P > .49), 72 hours (P > .99), and 96 hours (P > .99). P values for Rb were as follows: 0 hours (P < .01), 24 hours (P > .35), 36 hours (P > .19), 48 hours (P > .16), 72 hours (P > .99), and 96 hours (P > .99). (C) Levels of C/EBPα, CUGBP1, and HNF4α mRNAs after PH as ratios to β-actin mRNA. Experiments were performed with 2 biological replicates per genotype and time point and 2 technical replicates. Statistical analysis was performed with biological replicates. P values for CUGBP1 were as follows: 0 hours (P > .99), 24 hours (P > .99), 36 hours (P < .01), 48 hours (P > .85), 72 hours (P > .99), and 96 hours (P > .99). P values for HNF4α were as follows: 0 hours (P > .99), 24 hours (P > .09), 36 hours (P > .34), 48 hours (P > .99), 72 hours (P < .0001), and 96 hours (P > .99). P values for C/EBPα were as follows: 0 hours (P > .88), 24 hours (P > .59), 36 hours (P < .003), 48 hours (P < .004), 72 hours (P < .001), and 96 hours (P > .07). (D) Gank interacts and triggers degradation of TSPs in livers of LoxP mice, but not in the livers of Gank LKO mice. Gank was immunoprecipitated from nuclear extracts isolated from LoxP and Gank LKO livers and the IPs were probed with antibodies to CUGBP1, HNF4α, C/EBPα, and Rb. The bottom panel shows IP of E2F1 and Western blotting of IPs with antibodies to Rb. The most notable differences between LoxP and Gank LKO in the E2F1 IP were at 48–96 hours (illustrated with a black line). The Co-IP with C/EBPα had 1 technical replicate and all others were performed once. (E) Examination of post-translational modifications of Gank by 2D gel electrophoresis–Western blot assay. Nuclear extracts from livers of LoxP mice (0-hour time point and 48 hours after PH) were separated by 2D technique and probed with antibodies to Gank. Red arrows and circles show isoforms that are increased significantly in livers at 48 hours after PH. (F) A hypothesis for the inhibition of liver proliferation after PH in Gank LKO mice (see text). Two way analysis of variance ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, ∗∗∗∗P < .0001 LoxP vs Gank LKO. HRS, hours.