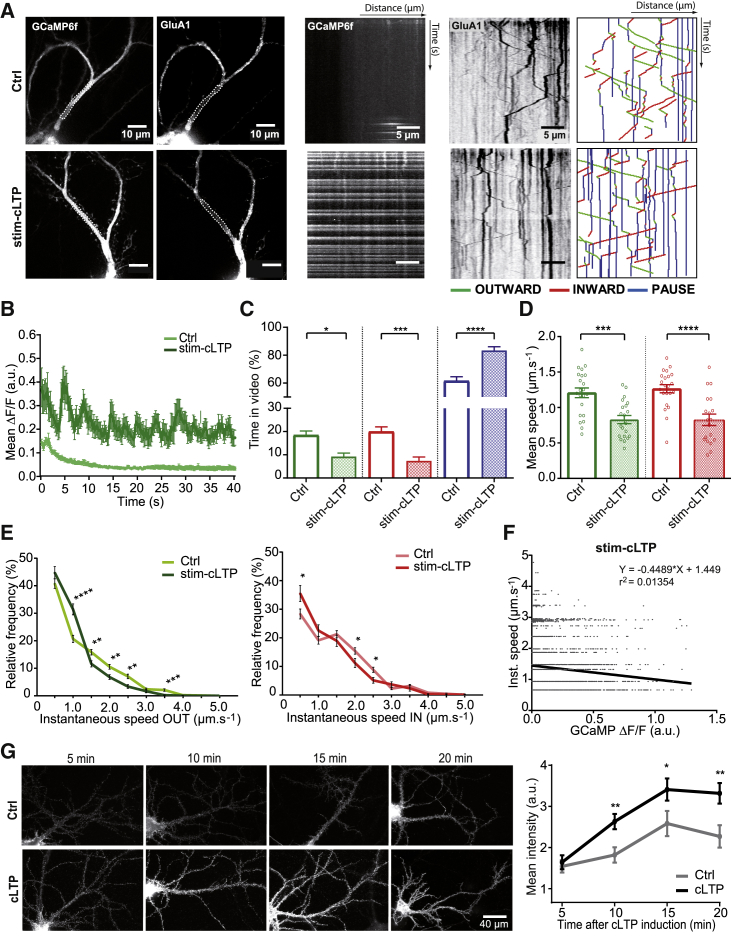
Figure 5.
cLTP Induction Decreases Vesicle Speeds and Increases Static Vesicle Frequency
(A) Images of 16-day neurons coexpressing ARIAD/TdT-GluA1 and GCaMP6f (left panels) and their associated kymographs (right panels) in basal condition (Ctrl, top panels) or during stim-cLTP (bottom panels).
(B) Variations of GCaMP6f fluorescence over time in basal condition (Ctrl) or during stim-cLTP. See also Figures S5B and S5C.
(C) Mean of the percentage of time spent in each state—outward (green), inward (red), pause (blue)—by a vesicle in both conditions. See also Figure S2C.
(D) Mean outward (green) and inward (red) velocities of GluA1-containing vesicles.
(E) Mean frequency distribution of the outward (green) and inward (red) instantaneous speeds of GluA1-containing vesicles (>200 values).
(F) Correlation between outward and inward instantaneous speeds and changes in the GCaMP6f fluorescence during stim-cLTP. See also Figure S5D for Ctrl.
(G) Images of neurons expressing ARIAD/GFP-GluA1 and their related quantifications. Staining has been performed on live cells with an anti-GFP antibody and showed the time course externalization of newly synthesized GFP-GluA1 analyzed between 5 and 20 min in basal conditions (Ctrl) or after stim-cLTP (cLTP).
For (B) to (F), mean ± SEM of 4 independent experiments (n = 22 cells). For (G), mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments (n > 30 cells). See also Tables S1 and S2.