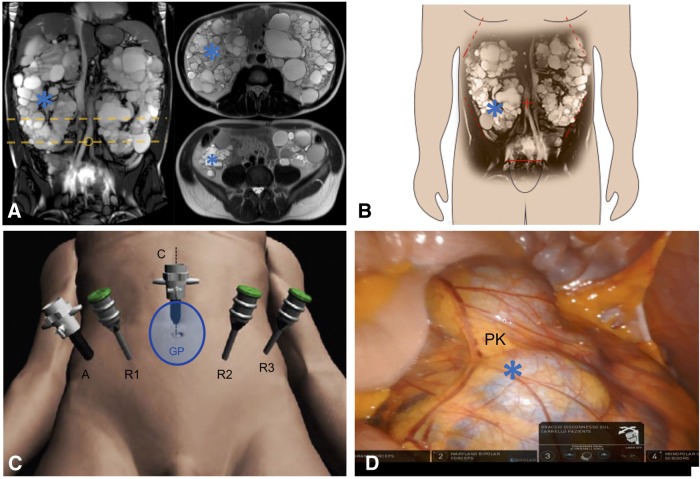
FIG. 1.
Overview of robotic kidney transplantation in our case. (A, B). MRI images showing the voluminous polycystic native kidneys. No space limitations at the level of transplantation site at the right iliac fossa were noted. The yellow dotted lines in A indicate the level of the transversal sections of the MRI images showed on the right side of A. (C) Trocar placement. A 4- to 5-cm midline periumbilical incision was made for the GelPOINT access device. A pneumoperitoneum of 12 mm Hg was established, and three 8 mm robotic ports and one 12 mm additional assistant port were inserted under vision in a modified RARP configuration. All trocars were positioned ∼3 cm downward on the same lines to obtain an increased working space far from the enlarged PKs. The patient was then turned to a 30° Trendelenburg position and the da Vinci Xi Robot® was docked on the lateral patient side. (D) Intraoperative snapshot showing the distal portion of the enlarged right PK (*): no space constraints were present at the level of the right iliac fossa. PK, polycystic kidney; RARP, robot-assisted radical prostatectomy.