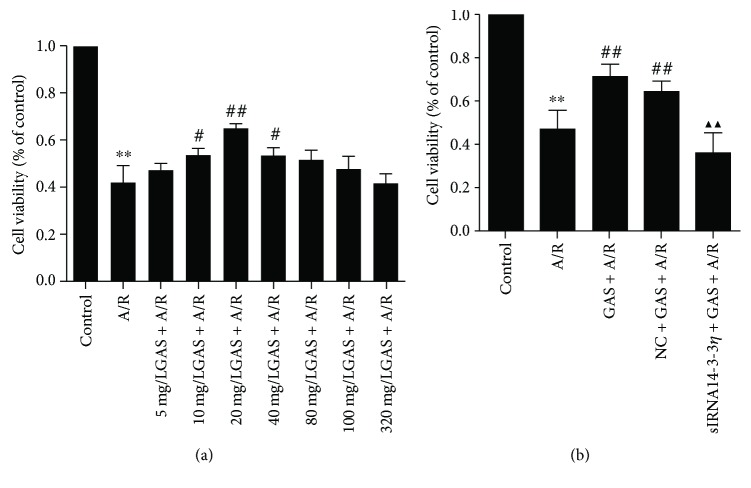
Figure 1.
Effects of gastrodin (GAS) on cell viability of H9c2 cells after A/R. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium (MTS) assay results showing that (a) the A/R group showed decreased cell viability of H9c2 cells (∗∗P < 0.01 versus control group). Pretreatment with different concentrations of GAS and the 20 mg/L GAS + A/R group exhibited the highest cell viability (#P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 versus A/R group). (b) The A/R treatment could decrease the cell viability of cardiomyocytes (∗∗P < 0.01 versus control group) and both the GAS + A/R group and the NC + GAS + A/R group had increased cell viability (##P < 0.01 versus A/R group), while siRNA14-3-3η abolished the effects of GAS on cell viability (▲▲P < 0.01 versus GAS + A/R group). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3).