Figure 1. Food and Aeroallergen Antigens in EoE.
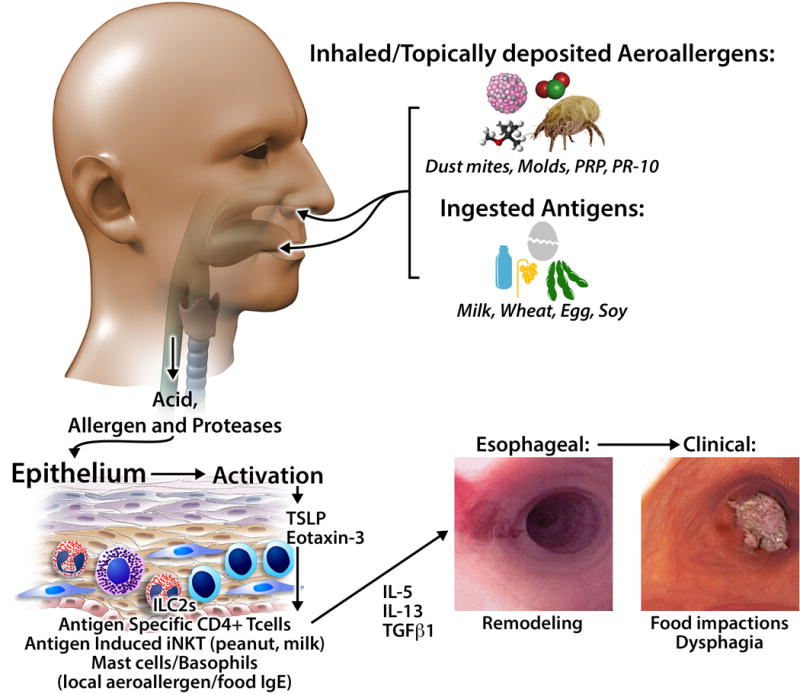
Ingested and inhaled antigens, in conjunction with acid and proteases, activate the epithelium to produce chemotactic and activating factors for innate (mast cells, basophils, iNKT, innate lymphoid cells) and adaptive (T cells) immune cells. Infiltrating cells can produce Th2 cytokines such as IL-13 and IL-4 as well as pro-fibrotic factors. Chronic inflammation initiates tissue remodeling with resultant dysphagia, food impactions, and strictures.
