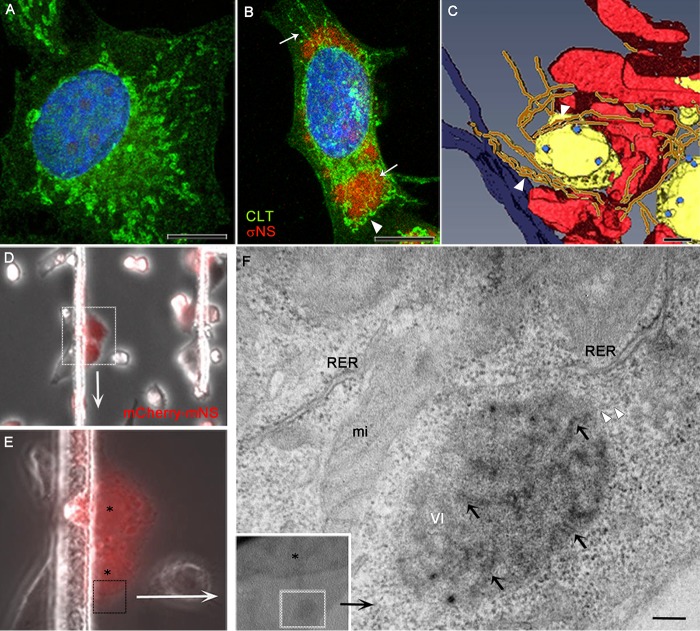
FIG 1 .
ER remodeling in reovirus-infected cells as visualized by confocal microscopy, 3D TEM, and CLEM. HeLa cells were adsorbed with reovirus T1L M1-P208S. At 14 h postadsorption, cells were immunolabeled with a rabbit anti-calreticulin (CLT) polyclonal antiserum, a mouse anti-σNS monoclonal antibody, and the corresponding secondary antibodies conjugated with Alexa 488 (green) and Alexa 594 (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (A) A mock-infected cell with normal ER cisternae. (B) Reovirus-infected cell with altered ER. White arrows indicate thin, fragmented ER membranes around and inside VIs. The arrowhead indicates thin, undulated ER attached to a VI. (C) TEM of serial sections and 3D reconstruction. VIs (yellow) containing viral particles (light blue) are surrounded by a network of abnormally thin, undulated ER cisternae (brown) that contact the VI (arrowheads). Mitochondria are colored in red, and the nuclear envelope is in dark blue. (D to F) CLEM of reovirus inclusions. HeLa cells engineered to express mCherry-μNS-MT were adsorbed with reovirus, incubated for 14 h, and imaged using bright-field and fluorescence microscopy. Cell nuclei are labeled with asterisks. Selected fluorescent cells (dashed squares) were imaged using TEM (F). An early VI is surrounded by rough ER (RER) and mitochondria (mi). Membranes distribute inside (black arrows) and at the periphery (arrowheads) of the inclusion. Bars, 10 µm (A and B), 500 nm (C), and 200 nm (F).