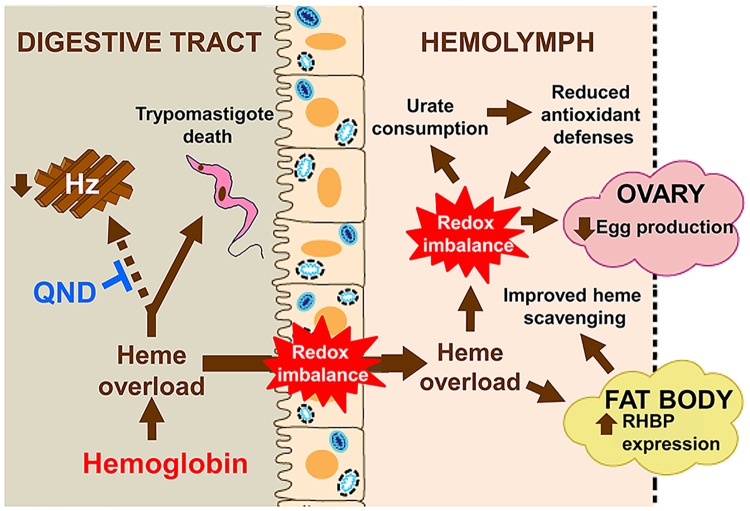
Fig 5. Schematic model of physiological consequences of blocked Hz formation in triatomine midgut.
In the presence of QND, heme derived from blood meal forms stable complexes with this drug, impairing Hz formation in the midgut lumen. Non-crystallized heme levels build up in the midgut causing cytotoxic effects to T. cruzi trypomastigotes. Excessive heme is transported to hemolymph through the midgut cells by hemoxisomes/residual bodies, causing redox imbalance and autophagy in the midgut. Heme accumulates in the hemolymph, increasing RHBP production, as a compensatory defense against "free" heme. However, this mechanism is overwhelmed, as the levels of urate drop. Redox imbalance has a direct effect on oogenesis, reducing egg production.