Figure 5.
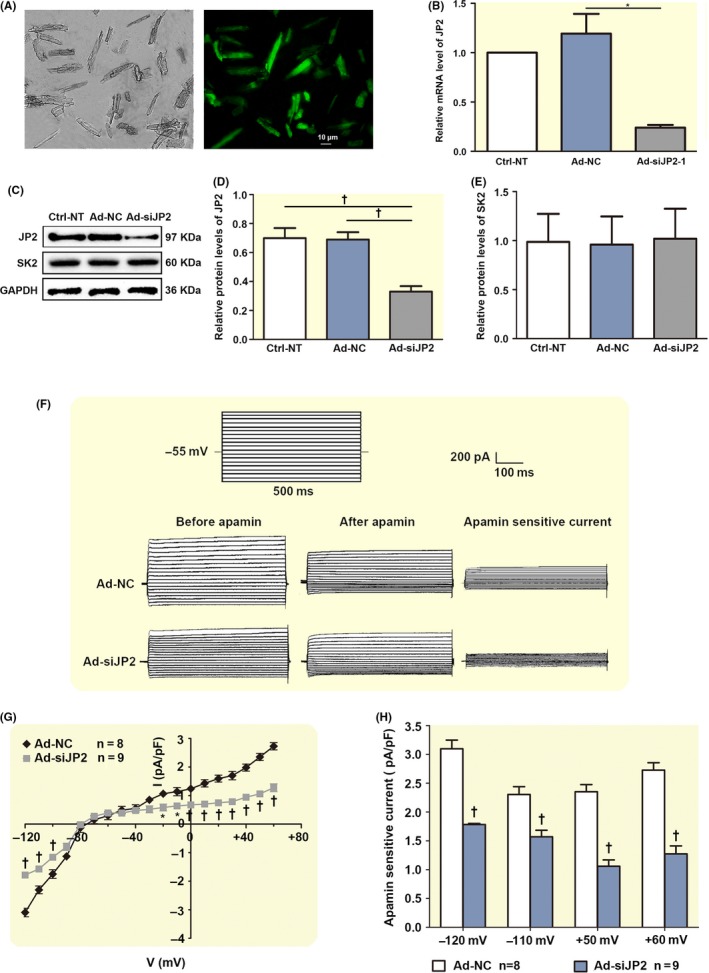
siRNA knockdown of JP2 depresses I K,Ca in the adult mouse cardiac myocytes. A, A photomicrograph of the fluorescent microscopy of EGFP expression in the isolated adult mouse cardiac myocytes after injection. B, A significant suppression of the levels of JP2 mRNA in the adult mouse cardiac myocytes transduced with Ad‐siJP2 vectors was observed using real‐time PCR compared to the scramble siRNA (Ad‐NC) myocardium and non‐transfected (Ctrl‐NT) myocardium (each n = 3). C, Western blot analysis showing the expressions of JP2 and SK2 proteins in adult mouse myocardium with different treatments. D, The bar graphs show significant decreases in the expression of JP2 in adult mouse myocardium transduced by Ad‐mediated siRNA specific to JP2. *P < .05 with respect to Ad‐NT or Ctrl‐NC groups (n = 5 per group). E, The bar graphs show no changes in the expression of SK proteins in siRNA‐infected adult mouse myocardium compared with Ad‐NT or Ctrl‐NC groups (n = 5 per group). F, Representative traces of I K,Ca evoked by depolarization steps from −120 mV to +60 mV from a holding potential of −55 mV in infected adult mouse cardiac myocytes. The protocol is illustrated above the current traces. Apamin‐sensitive currents in the right panels were obtained from the digital subtraction of the total current recorded in the presence and absence of apamin. G, Summary data of the current density‐voltage relationships showing a reduced apamin‐sensitive current densities in the adult mouse cardiac myocytes transduced with siRNA specific to JP2 (‡P < .01, †P < .01, *P < .05 vs control siRNA groups, n = 8 per group). F, The bar graphs show reduced I K,Ca in infected adult mouse cardiac myocytes when the test potentials were −120, −110, +50 and +60 mV, respectively. *P < .05, †P < .01 vs control siRNA groups (n = 8 for each group)
