Figure 4.
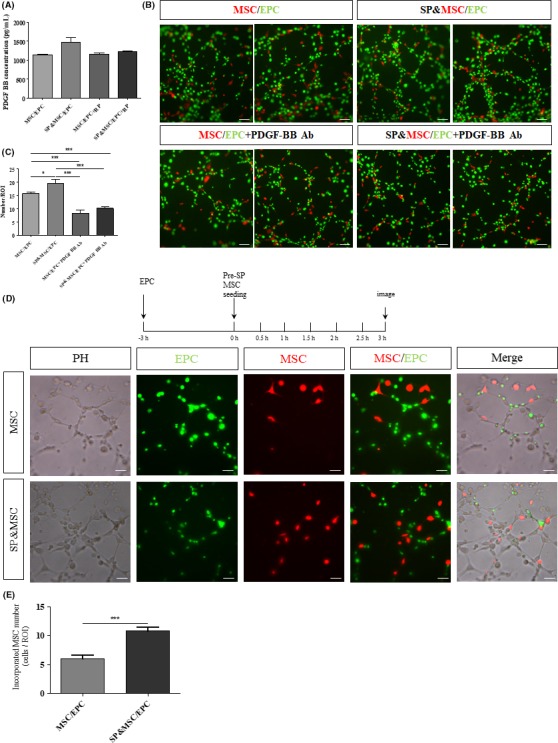
Inhibition of SP‐mediated PDGF‐BB induction by its receptor blockade and inhibition of tubular incorporation of BM‐MSCs by PDGF‐BB functional blocking antibodies. (A) ELISA analysis of PDGF‐BB in the coculture on Matrigel at 3 h. SP‐stimulated PDGF‐BB secretion was blocked by NK‐1 RP. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. (B,C) The cocultures of PKH‐red‐labeled BM‐MSCs and PKH‐green‐labeled BM‐EPCs were treated with SP and/or PDGF‐BB functional blocking Ab. At 3 h, the tubular network and tubular incorporation of BM‐MSCs were strongly diminished. The quantification analyses are presented as the mean ± SEM (*P < .05, ***P < .0005, student's t test). (D,E) Preferential tubular incorporation of SP‐pretreated BM‐MSCs. PKH‐green‐labeled BM‐EPCs were seeded on Matrigel at a density of 2 × 104 at 3 h in advance to reconstruct an endothelial tubular network. To test the effect of SP on BM‐MSC tubular incorporation capacity, PKH‐red‐labeled BM‐MSCs at a density of 2 × 103 cells/well with or without SP pretreatment for 3 h were plated. The quantitative analysis of tubular‐incorporated BM‐MSCs is presented as the mean ± SEM (***P < .0005, student's t test). Scale bar = 50 μm
