Figure 5.
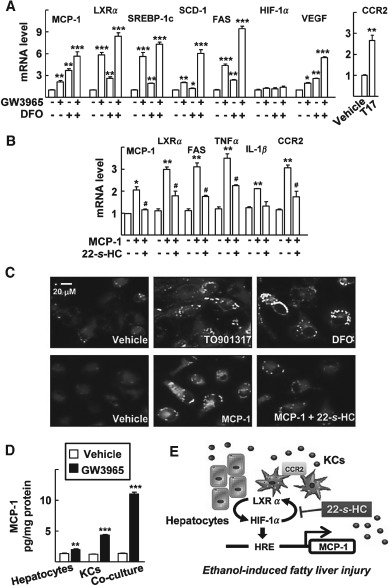
MCP‐1 induces lipogenesis in KCs via activation of LXRα and HIF‐1α. (A) KCs were treated with 1 µm GW3965 and/or 100 µm DFO for 24 h; mRNA levels of the indicated genes were analysed by qRT–PCR. (B) KCs were treated with 50 ng recombinant human MCP‐1 protein and/or 1 µm 22‐S‐HC for 48 h; numbers represent mean ± SD (n = 3); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.01 compared with vehicle‐treated control; # p < 0.05 compared with MCP‐1 treatment; statistical significance was evaluated by two‐way ANOVA. (C) KCs were treated with vehicle (DMSO), 100 µm DFO or 1 µm TO901317 for 48 h, or with vehicle (H2O), 50 ng recombinant human MCP‐1 protein and/or 1 µm 22‐S‐HC for 48 h; following treatment, lipid droplets were stained using Nile red and visualized by fluorescence microscopy (×400). (D) The primary hepatocytes were cultured with or without KCs for 4 h, and with vehicle or GW3965 1 µm for 48 h; MCP‐1 protein secreted into the culture supernatants was quantified by ELISA; numbers represent mean ± SD (n = 3); **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 compared with vehicle treatment; statistical significance was evaluated by two‐way ANOVA. (E) Schematic model for the activation of MCP‐1 by LXRα and HIF‐1α, which mediates ethanol‐induced fatty liver injury
