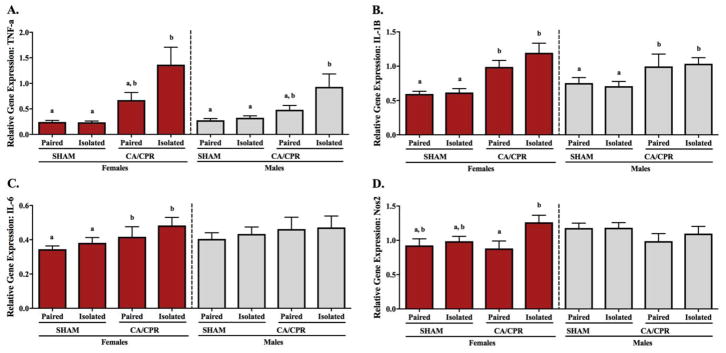
Figure 6.
Ninety-six hours after receiving the CA/CPR procedure, gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and Nos2 (i.e. iNOS) in the cortex were increased, a response that was exacerbated among animals that were socially isolated. Cortical expression of TNF-α in females and males was elevated 96 hours after CA/CPR, an effect that was exaggerated by isolation (A). IL-1β expression was also increased by the ischemic procedure, regardless of housing conditions or sex of the mice (B). In the cortex, IL-6 levels were upregulated following ischemia in the females, but remained unaffected in the males (C). iNOS expression on female mice was elevated following CA/CPR only in isolated mice, and did not vary among the males (D).