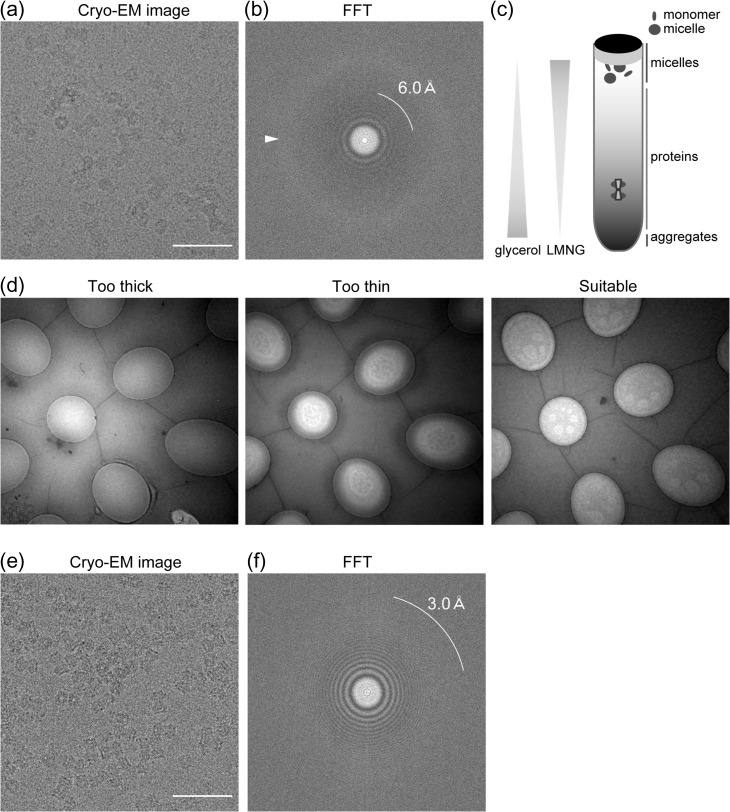
Fig. 2.
Cryo-EM data collection of wild-type INX-6 gap junction channels (modified from [24]). (a) Cryo-electron micrograph of INX-6 channels in thick ice containing 0.1% OGNG. Bar = 50 nm. (b) Fast-Fourier Transform image of (a). 6.0 Å resolution is indicated by the white line. Diffuse ice ring outside 6 Å resolution is visible (arrowhead), suggesting thick ice. (c) Schematic representation of GraDeR [35]. It should be noted that the glycerol concentration increases towards the bottom, and LMNG forms a reverse gradient in the ultracentrifuge tube. Free detergent micelles and monomers are removed by glycerol gradient centrifugation as only oligomeric INX-6 gap junction channels sink. (d) Search mode images of cryo-EM grids using purified INX-6 channels after GraDeR. Most holes have thick ice where only ambiguous particle images can be recorded (left). No particles are observed in excessively thin ice (middle), and suitably thin ice shows the contrast between the small white circles (right), and high-contrast particle images can be obtained from the grey area in these holes. (e) Cryo-electron micrograph of INX-6 channels after GraDeR showing side and top views. Bar = 50 nm. (f) Fast-Fourier Transform image of (e). 3.0 Å resolution is indicated by the white line. No ice ring is visible in this image.